If you're here on this gambling laws and regulations in Spain page, it's likely because Spain’s growing and profitable online gambling market has caught your attention, and you're eager to learn more about how to access it. This gambling market offers significant advantages for operators: a well-regulated and secure environment, and a highly engaged player base with solid opportunities for growth.
But like any market, compliance hurdles, licensing, associated costs, etc., must be handled diligently. That’s exactly what this article covers. Here’s your detailed guide on everything you need to know to successfully enter Spain’s thriving iGaming sector.
The History of Gambling in Spain
The earliest documented instance of gambling in Spain dates back to the 13th century with the emergence of card games like Primero, an early precursor to poker that quickly became a favourite among Spaniards. By the 18th century, gambling had taken on a more organised form, with the creation of the Spanish National Lottery in 1763 under King Carlos III marking a pivotal moment in Spain’s gambling history. At the time of its introduction, the lottery was not just a way to gamble; it was a way for the government to fund public initiatives while giving people a legal, structured form of entertainment.
As Spain entered the 20th century, gambling was initially viewed with suspicion and underwent periodic restrictions. The Ley de Represión del Juego of 1922 was an early attempt to clamp down on illegal gambling. Society’s appetite for betting was hard to restrain, though, leading to the first Gambling Act of 1977. This Act officially legalised casinos, bingo halls and lotteries, marking a significant turning point as gambling became a more accepted social pastime and one which would be more heavily regulated moving forward.
The 21st century saw the emergence of the digital age and, with it, the explosion of online gambling. Spain responded earlier than many other European nations by passing the Spanish Gambling Act of 2011. This initiative regulated the booming online gambling sector and established the Dirección General de Ordenación del Juego (DGOJ) to oversee licences and maintain the industry's integrity.
Timeline of Major Events
Over the centuries, gambling in Spain has evolved from an informal activity to a highly regulated industry. Below is a timeline of some of the major events that have shaped the development of gambling within the nation’s borders:
1763: Launch of the Spanish National Lottery by King Carlos III.
1922: The Gambling Repression Act to suppress illegal gambling.
1977: The Gambling Act legalising various gambling activities.
1981: Opening of state-regulated casinos in Madrid.
1990: Legalisation of sports betting across Spain.
1986: Launch of the National Lottery’s Christmas Draw.
2006: The legalisation of online poker.
2011: The Spanish Gambling Act, regulating online gambling.
2018: Restrictions imposed on online gambling advertising in Spain.
2020: Further restrictions on gambling advertising in the media.
2023: Strengthening of responsible gambling measures.
The Current Situation for Online Gambling
The current gambling market in modern-day Spain is one of the most sophisticated in Europe, with both retail and online gaming thriving under an advanced and well-regulated framework. With nearly 85% of Spanish adults engaging in some form of gambling each year, it is clear that gambling is not just a pastime, but it’s part of the cultural heritage of Spain.
From an operator's perspective, the situation for iGaming in Spain is characterised by a well-established regulatory framework. This governance is overseen by the General Directorate for the Regulation of Gambling (DGOJ). Fundamentally, online gambling in Spain is regulated by Law 13/2011 of the Spanish Gambling Act, which provides a clear structure for operators offering online gaming services within the country. In essence, the law applies to various gambling activities, including sports betting, poker, casino games and bingo, making Spain a mature and competitive market for both local and international operators.
As of 2024, Spain has continued its march towards enforcing strict advertising and operational regulations to protect players and promote responsible gambling. Notable examples include recent reforms that have increased restrictions on gambling promotions, including limits on bonus offers and advertising aimed at vulnerable groups. This has resulted in a more controlled environment, where operators must focus on compliance to maintain licences. Despite these limitations, the online gambling market remains active, with significant growth reported in sports betting and online casinos, showing continued market demand with no signs of slowing down.
Key Legal Activities in Spain
-
Online sports betting, poker, and casino games are all legal and well-regulated.
-
Online gambling is regulated at both the federal and regional levels in Spain. The national government oversees general licensing and compliance, while regional authorities manage local regulations, ensuring operators meet specific requirements within their respective jurisdictions.
-
Local and international operators can apply for licences, though they must meet strict regulatory requirements, including financial guarantees and operational controls.
-
Recent reforms have introduced further measures to curb unlicensed activities, ensuring a more secure and profitable environment for legal operators.
-
Players in Spain are taxed on gambling winnings that exceed €2,500. These winnings are treated as income and are subject to taxation, which must be declared on their personal tax return. However, losses are deductible up to the amount won. Lottery prizes exceeding €40,000 from SELAE and ONCE are taxed separately at 20%.
-
Sports betting remains the most popular form of gambling in Spain, with football betting preferred among Spanish nationals, followed closely by online casinos and poker.
Operational Requirements for Sportsbooks
Operators wishing to enter the Spanish market must obtain both a general (State level) and singular licence covering different gambling products. These licences are awarded for different timeframes depending on the type of licence.
General Licence
General licences will have a ten-year term and can be extended for a similar period of time (Article 10(6), Law 13/2011). These licences are issued through a competitive public tender process. Essentially, it is an umbrella licence that allows operators to offer a broad category of gambling activities. These categories include betting, contests, or other games like lotteries or casinos. Essentially, the general licence gives the operator permission to run a specific type of gambling activity in Spain, but it does not allow them to launch games immediately.
Singular Licence
A singular licence is more specific. After receiving a general licence, the operator must apply for a singular licence for each game or activity they want to offer, such as sports betting, poker or blackjack (Article 11(5), Law 13/2011). In other words, it is like getting permission to run a casino with the general licence and then applying for separate approvals to run specific games in that casino with the singular licence. Singular licences will be granted for a maximum period of five years and can also be extended for a similar period. Holders of singular licences must also hold a general licence.
The Public Tender Process
General licences for online gambling in Spain can only be obtained through public tenders initiated by the Ministry of Consumer Affairs upon the recommendation of the DGOJ. These tenders define the necessary criteria and terms. To prevent oversaturation in the market, the DGOJ may limit the number of licences for certain games, though no such limits have been imposed yet. Additionally, there must be at least 18 months between each licensing process, as per Article 10(1) of Law 13/2011.
For specific licences, operators who already hold a general licence can apply for them either concurrently or at any other time. The DGOJ oversees the issuance of these licences, following the guidelines outlined in Article 11 of Law 13/2011.
Operators should note that the tender process is highly competitive, and operators must demonstrate long-term financial stability and compliance with Spain’s anti-money laundering (AML) regulations, including a minimum paid-up share capital of €100,000 for betting and gambling licences.
Foundational Criteria for Market Entry
Spain's approach is considered one of the most regulated in Europe, which ensures operators meet high standards and only well-established and compliant operators can enter the market, which can be challenging for new entrants. Here are the foundational criteria that operators must meet:
1. Corporate Structure
Gambling businesses must be public limited or limited liability companies registered within the European Economic Area (EEA), with the sole corporate purpose of organising, marketing and operating gambling activities.
2. Financial Guarantee
To apply for a general licence, operators must provide a financial guarantee of €2 million for general licences, which may be reduced after the first two years of operation.
3. Technical Requirements
All operators must set up a specific website under a .es domain and ensure the technical systems for gambling meet the traceability and security standards set by Royal Decree 1613/2011, including the use of internal monitoring systems to track gambling transactions.
4. Licensing Fees
Operators entering Spain’s online gambling market face various costs for obtaining the necessary licences. In addition to the €7 million licensing fee for sports betting and casino games, several administrative fees are also required. These include a €20 fee for issuing register certification and €38,000 for technical reports ensuring compliance with all required standards.
Registration services cost €2,500, while each licence application incurs a €10,000 fee, with a €100 charge for each authorisation. Additionally, operators must cover auditing inspections or controls at a cost of €5,000. Finally, an administrative fee of 0.00075% of gross collections is charged to support the operations of Spain's regulator, the DGOJ, under Article 49(5) of Law 13/2011.
5. Physical Presence
Operators must have a registered address in Spain or another EEA country and be registered in the General Registry of Gambling Licences. While there is no strict requirement for a physical office in Spain, platforms must set technical infrastructure to comply with Spanish laws.
Licensing Costs for Market Entry
Entering the Spanish online gambling market comes with several financial commitments, beginning with the licensing fees and extending to regulatory and operational expenses. The primary cost drivers include the initial application fees, annual fees, taxes, and compliance costs. Spain's regulatory framework is designed to meet strict financial and operational standards before authorisation is granted.
General and Singular Licence Fees
Operators seeking to enter the Spanish market must first secure a general licence, which covers broad categories like betting and gaming. The application fee for a general licence is €38,000.
After securing the general licence, operators must apply for singular licences for specific activities (e.g. sports betting or poker), with an application fee of €2,500 per licence.
Additional Market Entry Costs
Beyond licensing, operators must factor in additional costs, such as:
-
Tax Obligations
Spain imposes a 20% Gross Gaming Revenue (GGR) tax, reduced to 10% of GGR for operators that become tax residents in the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla (Article 48(7), Law 13/2011). These rates make Spain a relatively competitive tax environment compared to other European markets. -
Compliance and Certification Fees
Operators must comply with Spanish regulatory standards, including technical certification from authorised testing bodies, which can cost up to €15,000, depending on the complexity of the platform. -
Operational Requirements
Operators are required to establish a local presence, either through a physical office or a legal representative. This comes with the cost of legal services and potential office expenses.
Key Regulatory Bodies Shaping Spain’s Gambling Framework
The Spanish gambling market is governed by several key authorities that substantially influence the industry's operation. Between them, their collective oversight creates a uniquely structured and tightly regulated environment by setting the rules, managing compliance, and ensuring fair play for both operators and players, with each authority serving a distinct role. Here is a description of the most prominent regulatory bodies in Spain:
Dirección General de Ordenación del Juego (DGOJ)
The DGOJ (Directorate General for the Regulation of Gambling) is the most influential body overseeing all gambling activities in Spain. It operates under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs and enforces gambling laws. It issues both general and singular licences and ensures operators meet demanding technical and operational standards. The Directorate General for the Regulation of Gambling also plays a crucial role in monitoring compliance standards, such as those that apply to anti-money laundering (AML) regulations. Thus, operators must adhere to Law 10/2010, which focuses on preventing money laundering and terrorist financing.
In practice, licensed operators must regularly submit reports to the DGOJ regarding player protection, technical audits, and financial activities to safeguard transparency. The DGOJ interacts closely with operators, conducting audits and investigating any irregularities or compliance breaches.
National Commission on Markets and Competition (CNMC)
The CNMC is an independent regulatory agency responsible for ensuring fair competition and market transparency across several sectors, including gambling. Its role in the gambling industry involves overseeing market practices to prevent anti-competitive behaviour so that operators adhere to Spain’s competition laws.
On a daily basis, the CNMC monitors the advertising and promotional activities of gambling operators to prevent unfair advantages or misleading promotions. It also intervenes in cases where operators may abuse their market position or engage in unethical practices such as collusion. The CNMC works in tandem with the DGOJ and other authorities to uphold fair market conditions and interacts with operators through audits, investigations, and enforcement actions when violations of market competition laws are suspected.
SEPBLAC (Spain’s Financial Intelligence Unit & AML Regulator)
SEPBLAC is Spain’s Financial Intelligence Unit responsible for overseeing anti-money laundering compliance across various sectors, including gambling. As part of its responsibilities, SEPBLAC ensures that gambling operators adhere to Law 10/2010, which mandates strict measures to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing. This includes monitoring financial transactions, conducting customer due diligence and reporting suspicious activity.
Operators are required to submit regular reports to SEPBLAC regarding any transactions that may indicate illegal financial activities. SEPBLAC also works closely with the DGOJ to audit the AML procedures of licensed operators and has the authority to impose sanctions or fines for non-compliance. In the overall scheme of things, its role is essential in maintaining the integrity of the Spanish financial system and preventing illicit activities within the gambling sector.
Spanish Tax Agency (Agencia Tributaria)
The Agencia Tributaria plays a key role in the Spanish gambling industry by overseeing the taxation of gambling operators and ensuring that both businesses and individuals comply with Spain's tax laws. For gambling operators, the agency is responsible for collecting taxes on gross gaming revenue (GGR), which currently stands at 20%.
The Spanish Tax Agency works closely with the DGOJ to affirm that licensed operators meet their financial obligations in as far as paying gambling taxes and other relevant fees. Furthermore, the agency enforces regulations on the taxation of player winnings, ensuring that individuals are taxed appropriately under the country's income tax laws. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including fines and the potential suspension of a gambling licence.
Spain's Betting Market Potential: Growth and Prospects
Spain’s online gambling market in 2024 is very lucrative and has abundant potential, therefore offering a promising destination for qualified and ambitious iGaming operators seeking further growth and expansion. With over 47 million residents and a steady rise in online gaming, it should come as no surprise the country’s digital gambling sector was valued at €850 million in 2022, which is projected to continue growing at an impressive rate. The combination of a passionate sporting culture, particularly in football, makes Spain a hotbed for sports betting operators keen to tap into the lucrative opportunities available in this central European jurisdiction.
The projected growth rate of the Spanish betting market is significant. According to recent reports, the Spanish gambling sector, including online sports betting and casino entertainment, has grown by an impressive 270% since 2014. Various factors, such as the increasing popularity of mobile gaming, fuel this growth. Moreover, recent reductions in GGR tax from 25% to 20% in 2018 have made the environment more attractive for established operators. While a 20% GGR tax may seem steep at first glance, the stability and security of operating in one of Europe’s most regulated markets usually outweigh the costs.
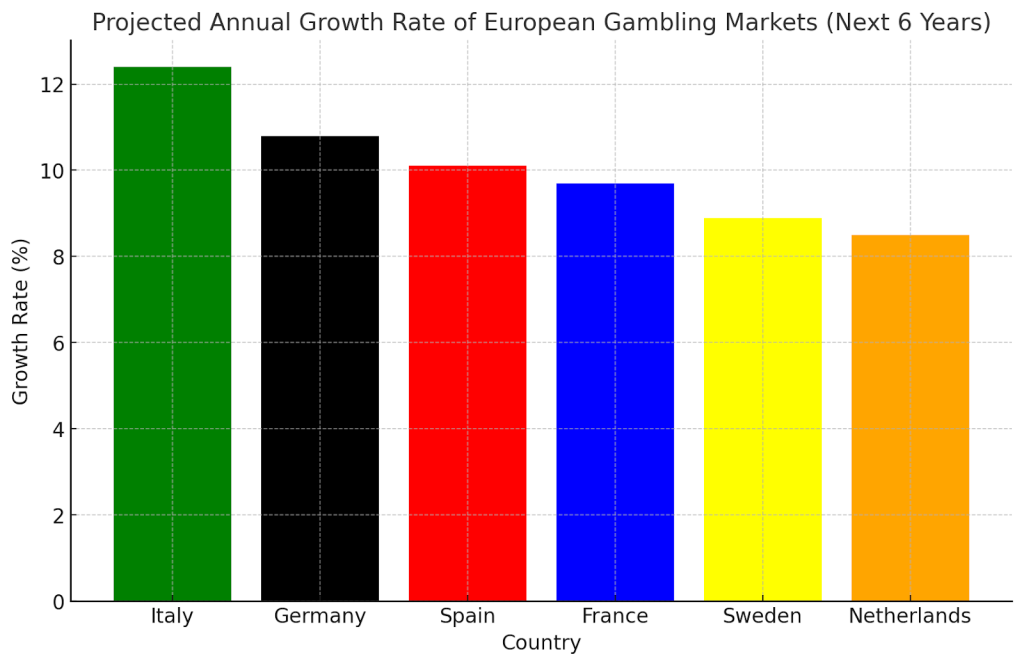
In comparison, the overall European sports betting market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 10.1% over the coming years. While smaller than giants like the UK, Spain's gambling market is catching up quickly, mainly due to its favourable regulatory environment. As Peter Murray, Director at Alexem Services, notes:
"The growth of sports betting in Spain is undeniable, driven largely by football’s popularity. As the market matures, it’s becoming a prime destination for operators looking to capitalise on a regulated, sports-focused environment."
Looking to the future, the expansion of mobile gaming, esports betting, and AI-driven personalisation strategies will undoubtedly push the industry forward. Operators that adapt to upcoming advertising restrictions and the growing demand for responsible gaming tools will find Spain fertile ground for long-term success. With that said, the Spanish market is set to become a significant player in Europe’s thriving online gaming sector, with projections showing continued growth well into 2025 and beyond.
Market Advantages
✔ Expanding online player base with a high 85% engagement.
✔ Strong and stable regulatory framework.
✔ Continued high growth projections.
✔ High demand for sports betting.
✔ Advanced mobile infrastructure and high internet penetration.
Market Disadvantages
✘ New advertising restrictions could limit marketing opportunities.
✘ Potential for increased regulation and compliance challenges.
Steps to Apply for a Gambling Licence in Spain
Here is a guide outlining the steps involved in applying for both general and singular licences, with essential requirements at each stage.
Step 1. Determine Licence Requirements
Before starting the application process, operators need to identify which licences are required for the gambling services they wish to offer. Spain has two primary types of licences:
-
General licences cover broad categories like betting, gaming, and lotteries. This licence is a prerequisite to offering specific gambling activities.
-
Singular licences are required for specific activities within each general category and are only obtainable after securing a general licence.
Step 2. General Licence Application Process
The application for a general licence can only be submitted during a public tender process, which the DGOJ announces periodically. This process involves several key steps:
-
Prepare documentation including:
-
Business plan detailing the scope of services, target market, and revenue projections.
-
Technical projections specifying the platform’s architecture, security measures, and responsible gaming protocols.
-
Financial reports demonstrating the company’s financial stability and ability to meet regulatory requirements.
-
Submit the application through the DGOJ’s licensing portal. A processing fee is required upon submission.
-
DGOJ Review
The DGOJ evaluates the application to ensure compliance with Spanish laws, including AML and player protection requirements. The review process can take several months, during which the DGOJ may request additional information or documentation.
Step 3. Singular Licence Application Process
Once a general licence is granted, operators can apply for singular licences targeted to the specific sports, casino or poker gambling activities they plan to offer. The steps include:
-
Prepare a singular licence application:
Operators must submit a singular licence application for each activity they wish to provide. This involves: -
A detailed description of the specific service.
-
Proof of the technical and financial capacity.
-
Compliance with defined standards.
-
DGOJ Technical Certification
Operators must ensure their technical systems (software, hardware, and player management systems) undergo certification by a DGOJ-approved testing laboratory.
Step 4. Establishing a Legal Presence in Spain
Foreign operators must have a legal representative or open a physical office in Spain. This helps facilitate compliance with local laws and allows easier interaction with regulators. Operators may need to:
-
Establish a legal representative or a local office.
-
Register with the Spanish Tax Authority (Agencia Tributaria).
Step 5. Meet Financial Requirements
Financial stability is a critical component of the application process. Operators must:
-
Provide bank guarantees to cover any potential liabilities related to player funds or regulatory fines.
-
Meet capital requirement’s demonstrating operators have sufficient capital reserves to support ongoing operations.
Step 6. Ongoing Compliance and Audits
Once the licences are granted, operators are subject to ongoing monitoring and audits to ensure continued compliance.
-
Regular Audits
Periodic audits to verify compliance with security standards, responsible gaming protocols, and data protection laws.
-
AML and Player Protection Compliance
Implementation and maintenance of AML systems and processes to ensure compliance and adherence to strict player protection rules.
Additional Regulatory Requirements
Moving forward, operators must stay up-to-date with ongoing regulatory developments, which may require adjustments to business practices. These include:
-
Advertising Restrictions
Ongoing adherence to advertising and marketing guidelines set by Spanish authorities.
-
Responsible Gambling Initiatives
Implementation of responsible gambling features, including self-exclusion tools and player protection measures to help mitigate the risks of gambling addiction.
For more detailed information and to begin the application process, operators can access the DGOJ’s official licensing portal.
Compliance Made Simple for Spanish Market Entry
Spain’s regulatory framework is designed for growth, but the path to compliance demands expertise. Altenar is fully certified for SB operations in Spain. Furthermore, our GLI-33 and ISO 27001-certified platform ensures your operations meet all legal standards to simplify market entry.
Reach out today and discover how we can help you confidently enter Spain and thrive in one of Europe’s fastest-growing markets.













