Overview Understanding Gambling Laws and Regulations in Germany
Germany's online gambling market, valued at nearly €2.9 billion in 2021, is experiencing significant growth and offers considerable potential for operators. A pivotal moment occurred in 2021 with the legalisation of online gambling through the Fourth Interstate Treaty on Gambling, which brought regulated online casinos, poker, and sports betting under a tightly controlled licensing system, a substantial shift from prior restrictions.
The Gemeinsame Glücksspielbehörde der Länder (GGL), fully operational since 2023, is now the central federal gambling authority responsible for issuing licences and enforcing compliance nationwide. Operators, including international ones, must meet demanding criteria such as demonstrating financial stability with a minimum €5 million security deposit, proving expertise, maintaining a physical office in the EU, and implementing robust responsible gambling and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) measures. Strict advertising restrictions also apply. Additionally, a 5.3% tax is levied on all stakes in sports betting, virtual slots, and online poker.
Despite the strict regulatory landscape and higher taxation compared to some other EU markets, Germany's substantial player base and high disposable income offer strong profit potential for those who comply. Operating without a legal licence carries serious risks, including fines, potential criminal charges, and increasing player lawsuits for reimbursement of gambling losses. This comprehensive framework is designed to ensure a stable, secure, and regulated market for continued expansion.
Now is the perfect time to explore Germany’s online gambling market and the potential it holds. With the recent legalisation of sports betting, the country has opened the doors to operators ready to make their big move into a sector valued at nearly €2.9 billion in 2021 and growing fast. But with great opportunity comes responsibility. Learning the laws and regulations of the local market might seem daunting, but that’s where knowledge becomes your ace in the hole.
This guide is here to help you understand the current legal landscape regulatory hurdles, and provide insights into Germany’s iGaming sector as it evolves.
Brief History of Gambling in Germany
As in many European jurisdictions, gambling first began to take root in Germany as a popular social activity back in the Middle Ages. Dice games and rudimentary forms of card games were played in local gatherings and public spaces. Moreover, nobility frequently engaged in high-stakes wagers during private meet-ups. One of the earliest documented gambling activities was the then-popular game of Glückshaus (House of Luck), a medieval dice game where players would roll dice to win coins or other prizes based on the outcome.
As the centuries passed, gambling became more than just a pastime - it grew into a structured part of German society. In the 19th century, grand casinos like the renowned Kurhaus in Baden-Baden emerged, entertaining Europe's elite. These establishments were seen not only as venues for chance but as symbols of wealth and sophistication, drawing visitors from across the continent.
Public sentiment towards gambling, however, was invariably mixed. While some saw it as harmless entertainment, others viewed it as a vice that needed regulation. This led to the introduction of various restrictions over the years. The aftermath of the World Wars, for instance, brought stricter oversight as governments sought to double down on gambling to maintain social order during uncertain times.
As Germany moved into the 21st century, the legal framework governing gambling began to take shape. The Interstate Treaty on Gambling (Glücksspielstaatsvertrag) 2008 marked a pivotal moment, regulating sports betting, lotteries, and casinos and introducing tighter controls over online gambling. This remained the status quo until a significant breakthrough in 2021 when Germany legalised online gambling through the Fourth Interstate Treaty. This shift finally acknowledged the change in public attitudes and market demands. In essence, it cemented Germany's role as a regulated yet thriving gambling market, setting the stage for continued growth in both retail and online sectors.
Timeline of Significant Events in German Gambling History:
1810 Establishment of Germany's first licensed casino in Bad Ems.
1872 The Imperial Gambling Act bans gambling houses.
1933 Nazi regime placed strict controls on gambling.
1950 Post-war reopening of casinos in West Germany.
1972 Legalisation of state-run sports betting and state lotteries.
2008 The Interstate Treaty on Gambling (Glücksspielstaatsvertrag)
2019 Treaty Amendments creating frameworks for licensing.
2021 The Fourth Interstate Treaty legalises online gambling.
2023 Newly-established gambling authority GGL operational.
2024 Further updates to online gambling regulations.
The Current Situation for iGaming
Germany presently operates under a comprehensive legal framework governing retail and online gambling. The Fourth Interstate Treaty on Gambling, enacted in 2021, has legalised online casinos, poker, and sports betting under a tightly controlled licensing system. This represents a significant shift in a country where online gambling was heavily restricted before the treaty’s adoption.
German citizens now have many legal gambling options available, including betting on permitted sports events, casino games, poker tournaments, and participating in state-run lotteries, both online and offline. However, strict player protection rules apply for online gambling platforms, including deposit limits and mandatory player identification checks aimed at promoting responsible gambling.
Operators wishing to offer gambling products and services in the German market must first obtain a licence issued by the newly established national gambling regulator, Gemeinsame Glücksspielbehörde der Länder (GGL). While the process is open to non-German international operators, the requirements are demanding. Operators must demonstrate full compliance with local regulations, including transparency in financial transactions, adherence to player protection measures, and restrictions on advertising.
Despite the legalisation of online gambling, the regulatory environment remains cautious, particularly regarding online casino games (with the exception of virtual slot machines and online poker). Online casino games are subject to state-level regulation and states may decide to operate them under a state monopoly or to issue licences. Licences are limited, and Section 22c(1) of the Interstate Treaty on Gambling states they may not exceed the number available to land-based casinos.
Retail casinos and sports betting outlets continue to operate under regional control, with each state maintaining its own specific regulations. This decentralised approach has made market entry complex for new gambling operators, but it also offers significant potential for those able to navigate the legal environment successfully.
Requirements and Regulations for Sportsbooks
Germany introduced sweeping reforms to its gambling regulations in 2021 with the Fourth Interstate Treaty on Gambling. The legislation has reshaped market conditions for online gambling, particularly for online sports betting businesses. As the market continues to evolve, private operators looking to enter the German market must meet demanding financial and operational requirements to succeed.
Here’s a breakdown of the key criteria that private operators must meet:
1. Financial Stability and Capital
Operators must demonstrate solid financial foundations, which include a minimum security deposit of €5 million, as stated by Section 4c(3) of the State Treaty. It must be in the form of an unlimited, directly enforceable bank guarantee from a credit institution domiciled in the European Union or in a state party to the Agreement on the European Economic Area. The security deposit may be increased by the authority granting the permit up to the amount of the expected average monthly turnover, up to a maximum of €50 million. This ensures that applicants have the resources to sustain operations and overcome any potential risks related to payouts and liabilities. In addition, proof of liquidity and long-term solvency is also required.
2. Proven Expertise and Reliability
According to Section 4a(1) b of the Glücksspielstaatsvertrag (GlüStV 2021), applicants and their key staff must prove they are trustworthy and skilled in running gambling operations. This ensures games are managed clearly and responsibly. Typically, the exact requirements for proving reliability and expertise are set out by the relevant licensing authority, which may request background checks, operational records, financial documents, or internal policies as part of their application review.
3. Physical Office Presence
A licensed operator is required to maintain a registered office in a member state of the European Union or a state party to the Agreement on the European Economic Area. If the office is not in Germany, the applicant must notify the competent authority of an authorised recipient and representative in Germany who is reliable as defined in No. 1 (b). This demonstrates the operator's commitment to the market, allows smoother communication and compliance with regulatory authorities, and ensures that legal or regulatory issues are resolved promptly.
4. Implementation of Responsible Gambling Measures
Operators must implement comprehensive measures to ensure responsible gambling and player protection. This entails establishing protocols like self-exclusion mechanisms, deposit limits, and tools that encourage moderation. Detailed reporting on player behaviour and spending patterns is necessary to protect vulnerable groups.
5. Compliance with AML Regulations
Precise AML laws apply, requiring operators to have robust systems for detecting and preventing money laundering activities. It includes monitoring player transactions, reporting suspicious activities, and adhering to Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols.
6. Advertising Restrictions
Marketing strategies are also heavily regulated. Operators must limit their advertising, especially during times when children might be exposed. All marketing content must comply with national guidelines that avoid targeting vulnerable individuals.
7. Payment of Licensing and Supervisory Fees
Operators are required to pay an initial licensing fee, which can reach €185,000 plus a percentage of the stakes, depending on the scope of the application. In addition, they must contribute an annual supervisory fee, generally calculated as a percentage of their gross gaming revenue (GGR). This fee supports the cost of regulatory oversight. See Section 9a (4) of the Interstate Treaty on Gambling for exact details of the fees involved.
8. Data Security and Player Information
German law requires operators to comply with data protection regulations, as described under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Operators must guarantee that player data is stored securely, with regular audits ensuring compliance with these data security standards.
Gambling Fees and Tax Regulation
The cost of entering the German online gambling market ranges from licence application fees to ongoing regulatory compliance and taxation. The Joint Gambling Supervisory Authority (GGL) is at the heart of the licensing process, established in January 2023 to centralise regulatory oversight. This authority is now the single entity responsible for granting online gambling licences, simplifying what was once a fragmented process across Germany’s 16 federal states. The GGL ensures that operators adhere to strict legal frameworks covering sports betting, virtual slot machines, and online poker.
Licensing
Licensing costs begin with a non-refundable application fee, which depends on the type and complexity of the licence. Operators must submit extensive documentation, including their responsible gambling policies, player protection measures, and plans for addressing gambling addiction.
Compliance costs
Operators can also expect several ongoing compliance costs arising from mandatory participation in the OASIS self-exclusion system, anti-money laundering protocols, and regular audits. Advertising is another area which is tightly regulated as it relates to gambling activities in Germany, requiring operators to submit marketing concepts in advance to ensure compliance with the Interstate Treaty on Gambling.
Taxation
The country imposes a 5.3% tax on all stakes in sports betting, virtual slots, and online poker, calculated based on total player wagers. While this rate is higher than some other EU markets, it reflects Germany’s commitment to maintaining a well-regulated gambling environment.
Regulatory Authorities
Germany's gambling industry operates under a tightly regulated framework enforced by key authorities. These regulatory bodies govern everything from licensing to compliance to anti-money laundering laws. Moreover, these influential regulators ensure that operators maintain high standards in their day-to-day activities.
Here is an overview of the top national authorities that oversee and regulate the gambling market in Germany.
Glücksspielbehörde der Länder (GGL)
Established in 2021 and fully operational in 2023, the GGL is Germany’s federal gambling authority, overseeing online gambling regulation nationwide. Its primary function is to issue licences, enforce compliance with local laws, and monitor operators for adherence to responsible gambling measures. The GGL also plays a vital role in combating unlicensed operators and ensuring player protection and transparency in operator practices. Its decisions and regulations significantly impact how both domestic and international operators conduct business within Germany’s borders.
It should be noted that operating without a legal licence in Germany presents some serious risks for online gambling operators. In addition to fines and potential criminal charges, operators face growing player lawsuits seeking reimbursement of gambling losses. Under Section 134 of the German Civil Code (BGB), contracts with unlicensed operators are deemed void, making it legally possible for players to claim refunds. Courts have increasingly ruled in favour of players, compelling unlicensed operators to repay substantial amounts, which is a trend likely to persist as regulatory scrutiny intensifies.
Regional Regulatory Authorities (State Level)
Germany operates under a federal system where each state (Länder) has its own authority responsible for regulating land-based gambling activities, such as casinos and sports betting shops. These regional bodies implement the Fourth Interstate Treaty on Gambling at the state level. They are responsible for issuing local licences, regulating the operation of physical gambling establishments, and monitoring advertising practices. Their role remains pivotal in enforcing gambling regulations specific to their regions, often working in tandem with the GGL for national cohesion.
There are 16 federal states in Germany, each with its own regional regulatory authority responsible for land-based gambling. Here’s a complete list of regional regulatory bodies:
| GERMAN STATE | REGIONAL AUTHORITY |
|---|---|
| Lower Saxony (Niedersachsen) | Ministerium für Inneres und Sport des Landes Niedersachsen |
| Hesse (Hessen) | Regierungspräsidium Darmstadt |
| Saxony-Anhalt (Sachsen-Anhalt) | Landesverwaltungsamt Sachsen-Anhalt |
| Brandenburg | Ministerium des Innern und für Kommunales Brandenburg |
| North Rhine-Westphalia (Nordrhein-westfalen) | Bezirksregierung Düsseldorf |
| Berlin | Senatsverwaltung für Inneres und Sport Berlin |
| Bavaria (Bayern) | Bayerisches Staatsministerium des Innern, für Sport und Integration |
| Baden-Württemberg | Ministerium für Inneres, Digitalisierung und Migration Baden-Württemberg |
| Rhineland-Palatinate (Rheinland-Pfalz) | Ministerium der Finanzen Rheinland-Pfalz |
| Thuringia (Thüringen) | Thüringer Landesverwaltungsamt |
| Saxony (Sachsen) | Ministerium für Inneres und Sport des Landes Sachsen |
| Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania (Mecklenburg-Vorpommern) | Ministerium für Inneres und Europa Mecklenburg-Vorpommern |
| Bremen | Senatorin für Finanzen Bremen |
| Bremen (Local) | Senator für Inneres Bremen |
| Schleswig-Holstein | Ministerium für Inneres, Bau und Gleichstellung des Landes Schleswig-Holstein |
| Hamburg | Behörde für Inneres und Sport Hamburg |
Federal Financial Supervisory Authority (BaFin)
Germany’s BaFin monitors financial transactions, ensuring operators comply with anti-money laundering and financial regulations. As gambling operators handle large transactional volumes, they must meet strict AML protocols, submit regular financial reports, and undergo regular audits. BaFin ensures that operators implement robust KYC processes and monitor transactions for suspicious activity. Non-compliance with BaFin regulations can result in fines, licence suspension, or even revocation.
Future Prospects and Emerging Trends
Germany offers significant prospects for online sportsbook and casino operators seeking to break into one of Europe’s largest and most promising gambling markets. With over 83 million residents and a growing appetite for online gaming, the potential for success is considerable. In 2021, the German online gambling sector was valued at around €2.9 billion, and it’s poised for further expansion as the legal framework matures and more players embrace regulated platforms.
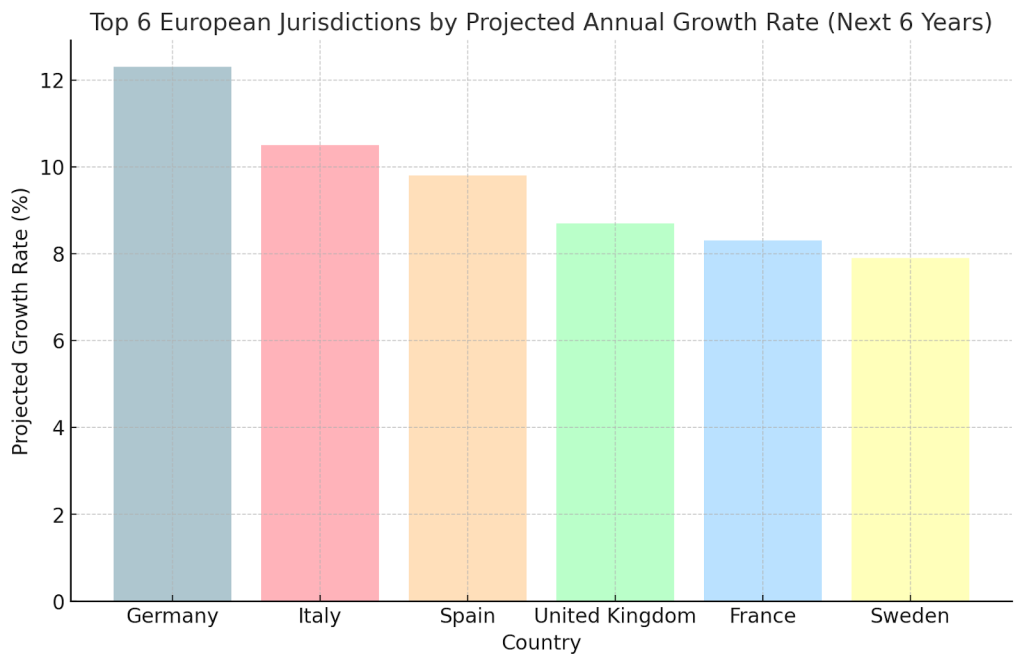
Though the regulatory environment is demanding, the German market does offer a stable and secure playing field. The Fourth Interstate Treaty on Gambling has brought much-needed structure, allowing operators to enter a market where player protection and responsible gambling are front and centre. The 5.3% tax on gross gaming revenue is higher in comparison with other European jurisdictions. Still, it is also fair to say that Germany’s massive player base and the disposable income levels of its citizens generally offset this, creating strong profit potential for those who comply with local rules.
While operators must navigate strict licensing and data protection laws, these hurdles help filter out non-serious competitors and ensure long-term market sustainability for investors. Future trends like the rise of mobile gaming further add to the exciting opportunities available in the recently liberalised online gambling market. For operators willing to invest in compliance and cutting-edge technology, Germany presents an exciting opportunity for growth in the iGaming world.
Market Advantages:
-
Expanding online player base
-
Clear regulatory framework
-
High disposable income of German citizens
-
Diverse gambling preferences
-
Strong mobile gaming growth
Market Disadvantages:
-
Strict licensing requirements
-
Limited advertising freedom
-
Complex regional regulations
How to Apply for a Gambling Licence in Germany
Applying for a gambling licence in Germany involves understanding and navigating various regulatory requirements depending on the type of gambling activity. The Interstate Treaty on Gambling (ISTG 2021) provides the foundational framework for licensing online gambling activities, including sports betting and virtual slot machines. However, the licensing landscape for online casino games such as roulette, blackjack, and baccarat remains a bit more complex. While some federal states, like Schleswig-Holstein and North Rhine-Westphalia, have opened their markets to private operators, others maintain a state monopoly. For example, Hesse and Thuringia have reserved online casino licences for state-run entities.
To apply for a gambling licence, operators must first decide which licence they require, whether for sports betting, virtual slots, or other forms of gambling. Since 2023, the Joint Gambling Supervisory Authority (GGL) has been responsible for issuing licences across all federal states, unifying the previously fragmented system. For sports betting and horse betting, applicants need to provide detailed information about the types of games offered, their operational structure, and the measures in place to protect vulnerable players.
Applications and guidelines can be found on the GGL’s official website, which offers operators direct access to the necessary documents and forms. When applying, applicants must submit multiple documents, including responsible gambling policies, terms and conditions, and data protection measures, via the official email portals for sports betting and horse betting.
Looking to Launch in Germany’s iGaming Market?
With Germany’s regulations evolving, operators have more opportunities than ever to enter its expanding market. Contact Altenar now to learn how our tailored products can help you grow your brand once your licence is secured.
Disclaimer
This information is not intended to be legal advice and is solely extracted from open sources. It should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional legal advice and Altenar does not accept any liability in relation to its use.













