Disclaimer
This information is not intended to be legal advice and is solely extracted from open sources. It should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional legal advice, and Altenar does not accept any liability concerning its use.
Georgia has become a focal point of debate over the potential legalisation of gambling activities in recent years. With growing public interest and legislative efforts sparking widespread attention, the state’s gambling sector is at a crossroads. This text digs deeper into Georgia’s unique approach to gambling regulation, explores its historical journey, and sheds light on the current state of play.
Find clarity on the important topics surrounding key regulatory authorities, lotteries, charitable gaming, the legal deployment of Coin Operated Amusement Machines (COAM), and the evolving discussions surrounding sports betting and casino legalisation.
From Lotteries to Legal Battles - The History of Gambling Legislation in Georgia
Few states have walked the tightrope between public opposition and economic potential as much as Georgia has. The state conducted land lotteries in the early 19th century, marking its initial engagement with organised games of chance. However, as the century progressed, public sentiment shifted towards conservatism, leading to inflexible anti-gambling laws that persisted well into the 20th century.
A significant turning point occurred in 1992 when Georgia voters approved a constitutional amendment establishing the Georgia Lottery Corporation. This state-run lottery was designed to fund educational initiatives, notably the HOPE Scholarship, and has since become a model for other states. Despite the lottery's success, efforts to expand further have faced considerable challenges.
There has been a growing momentum towards legalising sports betting in recent years. Advocates argue that liberalising gambling activities could generate substantial tax revenue earmarked for Georgia’s popular Scholarships and Pre-Kindergarten programs.
However, legislative efforts have encountered significant hurdles. In 2024, Senate Resolution 579, which aimed to legalise sports betting in Georgia, successfully passed the Senate but stalled in the House. Despite multiple attempts to push the bill forward, the House Higher Education Committee failed to act before the final legislative deadline. On March 27, 2024, the committee left open the possibility of a last-minute vote the following day, but the bill required a full legislative tour through both chambers of the General Assembly before the session adjourned.
Had the House approved the legislation, it would have required a two-thirds vote in the Senate or a conference committee to reconcile differences before final approval. Even if lawmakers had managed to pass the bill, it still would have needed voter approval in a statewide referendum in November. With this window now closed, Georgia's next opportunity to amend its constitution for sports betting will not come until 2026.
The proposed legislation would have authorised the Georgia Lottery Commission to issue up to 16 mobile sports betting licences, with nine reserved for professional sports teams and venues and seven allocated through a competitive bidding process. The failure to enact these measures means that Georgia remains without legal sports betting, leaving a significant gap in potential tax revenue and economic growth compared to neighbouring states that have embraced the industry.
Public attitudes towards gambling in Georgia have been predominantly conservative, with many citizens expressing concerns about the potential social costs associated with expanded gambling. Faith-based and social groups have been vocal in their opposition, citing the risks of addiction and other societal harms.
Timeline of Gambling Events and Legislation
Below is a timeline highlighting pivotal moments and regulations that have shaped the state's approach to gambling:
1805: Land lotteries were initiated in Georgia as a state-run programme to distribute land, marking an early instance of organised gaming.
1878: Anti-gambling laws were enacted, imposing statewide restrictions on gambling activities.
1945: Slot machines were banned, leading to their removal across the state.
1976: Charitable gaming was legalised, allowing nonprofits to conduct raffles and bingo under specific conditions.
1992: The Georgia Lottery was established and designed to fund educational initiatives such as the HOPE Scholarship.
1993: The state sold its first lottery ticket, officially beginning Georgia Lottery operations.
2008: Lottery funds supported the expansion of the HOPE Scholarship, broadening access to higher education across the state.
2018: A proposal to legalise casinos was rejected due to public and legislative resistance.
2021: Bills to legalise sports betting were introduced in the state legislature, igniting debates on gambling expansion.
2023: The debate over sports betting intensified as advocates renewed efforts to pass legislation.
2024: Proposed sports betting bills failed to pass in the House, delaying progress towards legalisation.
The Situation for Gambling in 2025
Building upon Georgia's historical journey with gambling, the state maintains a conservative stance towards both land-based and online gaming activities. Currently, the Georgia Lottery is the only primary legal form of gambling, funnelling its proceeds into educational programs. Charitable gaming, including raffles and bingo conducted by nonprofit organisations, is also permitted under specific regulations.
Unlike states such as Illinois, Georgia does not offer land-based gambling at racetrack casinos, online casino gaming, or poker. Sports betting, both at physical locations and online platforms, also remains illegal. Recent legislative efforts to introduce sports wagering have encountered obstacles. In 2024, bills such as SR 579 and SB 386, two significant pieces of legislation aimed at legalising sports betting, passed the Senate but failed to clear the House. Ultimately, this has delayed the possibility of legal sports betting until at least 2026.
The current legal framework offers limited opportunities for gaming operators and sports betting enthusiasts in Georgia. The absence of legal sports betting means potential tax revenues remain untapped, and bettors lack regulated and legal avenues for wagering. As neighbouring states continue to expand their gambling offerings, the pressure mounts on Georgia to reconsider its restrictive policies.
While the state’s gambling landscape remains limited, ongoing legislative discussions indicate a potential shift in the coming years. Stakeholders and industry operators should continue to monitor developments closely, as changes could introduce new opportunities and considerations for operators and bettors alike.
Legal Challenges and Public Sentiment
Georgia's constitution explicitly prohibits most forms of gambling, including casino gaming and pari-mutuel betting. This prohibition is rooted in Article I, Section II, Paragraph VIII of the Constitution of the State of Georgia, which bans lotteries and other forms of gambling, with specific exceptions such as the state-run lottery established in 1992.
Legalising additional gambling activities requires a constitutional amendment, needing a two-thirds majority vote in both legislative chambers and voter approval in a statewide referendum. This rigorous procedure has historically posed a significant barrier to gambling expansion.
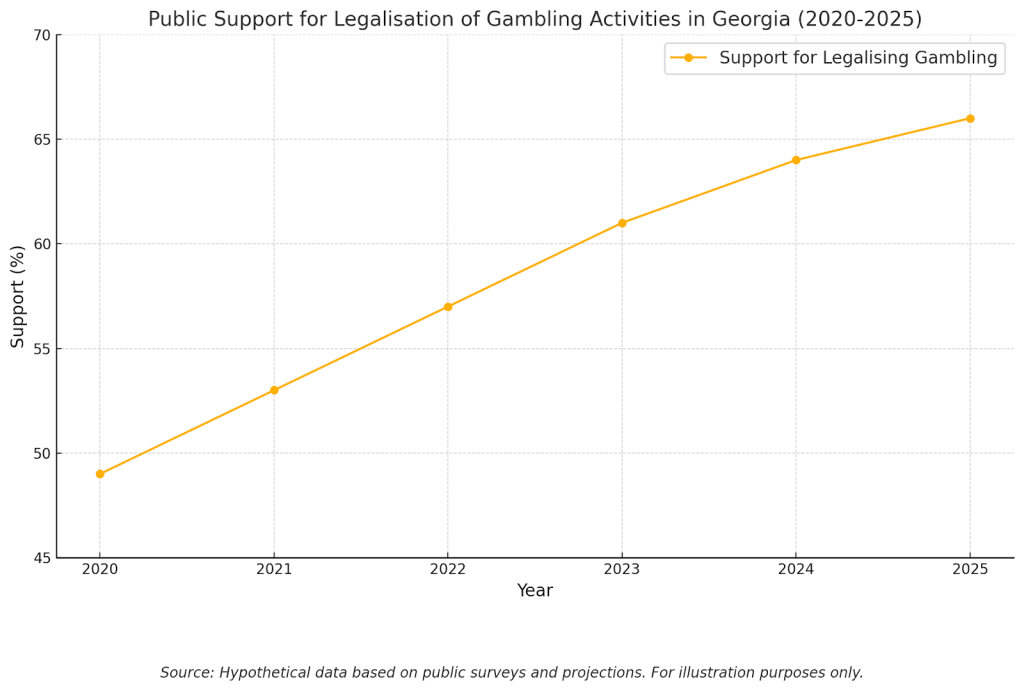
Despite these legal barriers, public opinion in Georgia appears to be shifting. A 2022 survey revealed that approximately 60% of likely voters support legalising casino gambling, while around 46% are in favour of online sports betting.
Furthermore, a 2023 poll indicated that 66% of respondents favour legalising casinos, with an even higher 85% supporting the idea of allowing voters to decide on the matter. These trends suggest a growing public openness to gambling, which could influence future legal efforts. However, the path to legalisation remains complex, requiring not only public support but also significant legislative action to amend the state constitution.
Economic Lessons - A Roadmap for Georgia?
Georgia stands on the threshold of potential economic transformation, with neighbouring states offering a blueprint for success through gambling liberalisation. Tennessee’s bold move to legalise online sports betting in 2020, for example, has had a significant impact on the state's revenues. Major operators like BetMGM, FanDuel, Caesars, and DraftKings quickly entered the market, driving significant economic gains and establishing Tennessee as a leader in the southern United States.
Moreover, North Carolina’s recent expansion into online sports betting in 2024 demonstrates how regulatory progress can unlock substantial financial rewards. With top US platforms already active, the state has tapped into a lucrative market, generating millions in tax revenue and expanding entertainment options for residents.
For Georgia, these success stories are a glimpse into a possible future. By opening its gambling market, the state could attract top-tier operators, advance innovation, and generate significant additional revenue streams. This would not only diversify the state’s economy but also provide meaningful support for education and public initiatives.
Regulatory Gambling Authorities
Regulating gambling activities in Georgia involves a coordinated effort by key authorities responsible for oversight, compliance, and enforcement. These institutions work to maintain legal integrity, ensure fair operations, and contribute to state initiatives.
Georgia Lottery Corporation (GLC)
The Georgia Lottery Corporation was established in 1992 following a statewide referendum. Created to oversee and operate the state lottery, the GLC primarily aims to generate revenue for educational initiatives. It administers various lottery games, ensuring compliance with state regulations while managing ticket sales and prize distribution. Since its inception, the GLC has been a substantial source of funding for education, contributing billions of dollars to the cause.
In its regulatory capacity, the GLC collaborates with the Georgia Bureau of Investigation's Commercial Gambling Unit (CGU) to enforce laws related to Coin Operated Amusement Machines (COAM) and other gambling activities. This partnership ensures that all licensed operators comply with regulations to prevent underage and problem gambling.
The GLC's firm oversight and commitment to integrity have been instrumental in maintaining public trust and ensuring that lottery operations contribute positively to Georgia's educational sector. Its interactions with other regulatory bodies and gambling operators are guided by a framework that prioritises transparency, compliance, and the responsible allocation of funds.
Georgia Bureau of Investigation (GBI) – Commercial Gambling Unit (CGU)
Established in August 2013 at the request of the Governor and the Georgia Lottery Corporation, the Georgia Bureau of Investigation's Commercial Gambling Unit (CGU) is dedicated to enforcing the state's commercial gambling laws, particularly those relating to Coin-Operated Amusement Machines (COAM) prevalent in convenience stores and similar establishments. These machines are legally permissible, provided they are appropriately licensed through the Georgia Lottery Corporation.
The CGU strictly prohibits cash payouts and ensures that credits earned from COAM play are redeemed solely for in-store merchandise, fuel, or lottery tickets. By conducting thorough investigations and collaborating with other agencies, the CGU maintains the integrity of Georgia's gambling environment, ensures operator compliance, and safeguards against illegal gambling activities.
Georgia Department of Revenue (DOR)
The Georgia Department of Revenue oversees taxation and financial compliance of legal gambling operations, ensuring that all revenues are accurately reported and appropriate taxes are collected. This includes tax administration related to the COAM.
DOR collaborates closely with other agencies, such as the Georgia Lottery Corporation and the Georgia Bureau of Investigation's Commercial Gambling Unit regularly to maintain the integrity of the state's gambling environment. By enforcing compliance with state laws and regulations, the DOR ensures that gambling operators adhere to financial obligations, contributing to the state's revenue and supporting public initiatives.
Future Outlook for Legal Sports Betting and Casino Gaming
Georgia’s potential as a legal gambling destination is a topic of growing interest. The state’s sizable population of over 10 million represents an untapped market for iGaming operators. While gambling remains largely prohibited, discussions around its legalisation are intensifying. Should the state embrace regulated gambling, early adopters in the market stand to benefit significantly.
The current legislative environment has seen repeated attempts to introduce sports betting and casino gambling. Although recent bills have faltered, they nonetheless reflect a growing momentum towards change. States like Tennessee and North Carolina, where online and land-based sports betting has thrived, offer compelling case studies. Georgia could follow a similar trajectory, leveraging its population size and interest in sports to fuel a profitable gambling sector.
It is worth considering that legalisation could unlock significant economic rewards. Experts suggest that tax revenue from regulated gambling could exceed $1.5 billion annually, funding essential state initiatives in public services and infrastructure. Moreover, the advent of mobile sports betting could position Georgia as a hub for digital innovation, attracting operators eager to implement cutting-edge platforms and user experiences. Future opportunities might include cross-state poker liquidity pools, creating a competitive edge for operators wishing to cater to both local and regional players.
However, significant barriers remain. A strong anti-gambling lobby and cultural conservatism have historically slowed progress. Yet, these concerns could be mitigated with the right regulatory framework prioritising responsible gambling and transparency. Georgia’s infrastructure and potential tax incentives make it an enticing prospect for operators ready to bid their time, overcome the early challenges, and jump on opportunities as they arise.
All things considered, while the future of gambling in Georgia remains uncertain, it holds immense promise. Operators willing to invest in early market entry strategies and adapt to potential regulatory changes could reap substantial rewards. For this reason, Georgia’s potential evolution into a regulated gambling market is a development worth watching closely.
Risks and Rewards for First Movers in a Liberalised Market in Georgia
The decision to enter Georgia’s gambling market early (should it become liberalised in 2026) requires a balanced understanding of its potential benefits and challenges. Here are the most significant advantages and limitations of early market entry.
Market Advantages
The state’s demographic and economic profile suggests strong long-term opportunities if policymakers revisit the issue in 2026. Key advantages include:
-
Large Untapped Market: With over 10 million residents and no legal sports betting, Georgia presents a significant opportunity for operators if the regulatory framework changes. The demand for sports wagering remains high, as evidenced by active legislative discussions and strong public interest.
-
Established Lottery Infrastructure: The Georgia Lottery Corporation, which was set to regulate sports betting under the 2024 proposal, has decades of experience overseeing gambling activities. This existing framework could facilitate a swift rollout if legislation passes in the future.
-
Strong Sports Culture: Home to major franchises such as the Atlanta Falcons (NFL), Braves (MLB), Hawks (NBA), and United (MLS), Georgia has a deeply rooted sports following. The proposed model of granting licences to professional sports teams highlights the potential for a highly engaged betting audience.
-
Proven Success in Neighbouring States: Tennessee and North Carolina have successfully implemented regulated sports betting, generating substantial tax revenues. Their models serve as a roadmap for Georgia, demonstrating how regulatory frameworks can drive economic growth while addressing concerns about responsible gambling.
-
Potential for Competitive Market Entry: The proposed 16-licence model, with seven open licences available through a competitive bidding process, could create a dynamic environment for new entrants. Operators that position themselves early could gain a foothold in a market that is expected to be highly lucrative once legalised.
Market Disadvantages
Georgia remains a complex jurisdiction for gambling expansion. While opportunities exist, operators should carefully assess the long-term outlook and legislative climate before committing significant resources.
-
Regulatory Uncertainty and Delays: With the failure of the 2024 sports betting legislation, the next opportunity for a constitutional amendment will not arise until 2026. This prolonged timeline creates uncertainty for operators seeking early entry.
-
Strong Anti-Gambling Resistance: Despite growing public support for legal gambling, conservative opposition remains a formidable barrier. Faith-based organisations and social groups continue to influence lawmakers, slowing the momentum for legislative change.
-
Potentially High Licensing and Tax Costs: The 2024 proposal outlined a model that allocated 16 mobile sports betting licences, with some reserved for professional sports franchises. If a future bill follows a similar structure, limited licence availability could drive up costs for operators looking to enter the market.
Coin-Operated Amusement Machines (COAMs)
Coin-operated amusement Machines (COAMs) represent a unique aspect of Georgia's regulated gaming environment. Unlike traditional casino-style gaming, COAMs are skill-based or redemption machines that operate under strict oversight from the Georgia Lottery Corporation (GLC). They are commonly found in convenience stores, restaurants, and other licensed establishments across the state.
Georgia law categorises COAMs into Class A and Class B machines:
-
Class A Machines: These include traditional arcade-style games like pinball, crane machines, and non-cash prize redemption games. These machines do not offer monetary rewards.
-
Class B Machines: These machines allow players to accrue points that can be redeemed for in-store merchandise, fuel, or lottery tickets—but never for cash payouts, as cash prizes are strictly prohibited.
To legally operate COAMs, business owners must obtain appropriate licences from the Georgia Lottery Corporation, which regulates the industry to ensure compliance. The Georgia Bureau of Investigation's Commercial Gambling Unit (CGU) works alongside the GLC to enforce laws preventing illegal gambling activity and ensuring that COAM operators meet state requirements.
While COAMs provide an additional revenue stream for licensed businesses, their classification as non-casino gaming machines means they operate under different legal frameworks than sports betting or commercial gambling enterprises. Operators interested in COAMs should ensure full compliance with Georgia’s licensing and operational guidelines, as failure to adhere to regulations can result in penalties or revocation of licences.
Compliance and performance go hand in hand with Altenar’s sportsbook technology. Let us help you succeed in regulated US markets where sports betting is currently legal.
Contact us now to learn more about our tailored solutions for your multi-state operations.
Disclaimer
This information is not intended to be legal advice and is solely extracted from open sources. It should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional legal advice, and Altenar does not accept any liability concerning its use.













