While traditional casinos lose ground, a new wave of Dutch players is embracing eSports, live dealer games, and mobile-first betting. This shift presents an opportunity for progressive operators to capture market share in one of the world’s top-eight sports betting markets, where high-value bettors drive consistent revenue.
Yes, the Dutch market is evolving fast, and the headlines warn of tougher regulations and stiffer competition — but opportunities remain for those who know the market and how to navigate its evolving gambling laws.
DISCLAIMER
This information is not intended to be legal advice and is solely extracted from public sources. It should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional legal advice, and Altenar does not accept any liability for its use.
The History of Gambling in the Netherlands
Long before digital sportsbooks and modern casinos, the Dutch had a passion for betting. In the 14th century, games of chance were a social highlight, providing an early glimpse into what would one day become a thriving, highly regulated industry. However, it wasn’t until 1726 that the Dutch government took its first major step toward regulation, establishing the Staatsloterij, one of the world's oldest continuous lotteries. This move signaled the first attempt to channel gambling into state-controlled avenues, reflecting both a desire to regulate the activity and to use it as a source of public revenue.
By the mid-19th century, as gambling became more widespread, concerns about addiction and fraud prompted calls for greater oversight. The government responded with early regulatory measures aimed at restricting unlicensed operators while allowing state-approved forms of gambling to flourish. Still, a proper legal framework didn’t take shape until 1964, with the introduction of the Betting and Gaming Act (Wet op de Kansspelen). This landmark legislation granted the state control over gambling operations through a regulated licensing system, balancing consumer protection with controlled market access.
The biggest shift came in 1976, when Holland Casino opened its doors in Zandvoort, marking the beginning of a state-controlled casino network. Over time, the venue was granted exclusive rights to operate land-based casino operations, establishing a government-sanctioned monopoly on physical gambling. The move aimed to prevent illegal gambling dens from thriving while ensuring that gambling profits contributed to public funds rather than private interests.
For decades, the Dutch gambling market remained tightly controlled, but the rise of the internet in the 2000s posed a new challenge. Unregulated online gambling platforms gained popularity among Dutch players, creating a legal gray area that the 1964 Act was ill-equipped to address. Recognizing the need for reform, policymakers began modernization discussions in 2008, culminating in the first draft of the Remote Gambling Act (KOA) in 2012. This new legislation aimed to bring online gambling under official regulation, ensuring player protection and responsible gaming practices.
After years of legislative refinement, the Remote Gambling Act was finally enacted on April 1, 2021, paving the way for licensed international operators to enter the Dutch market. But it wasn’t until October 1, 2021, after a rigorous licensing process, that the first legal online gambling platforms officially launched. This signaled the beginning of a new era for Dutch gambling.
Key Events Timeline
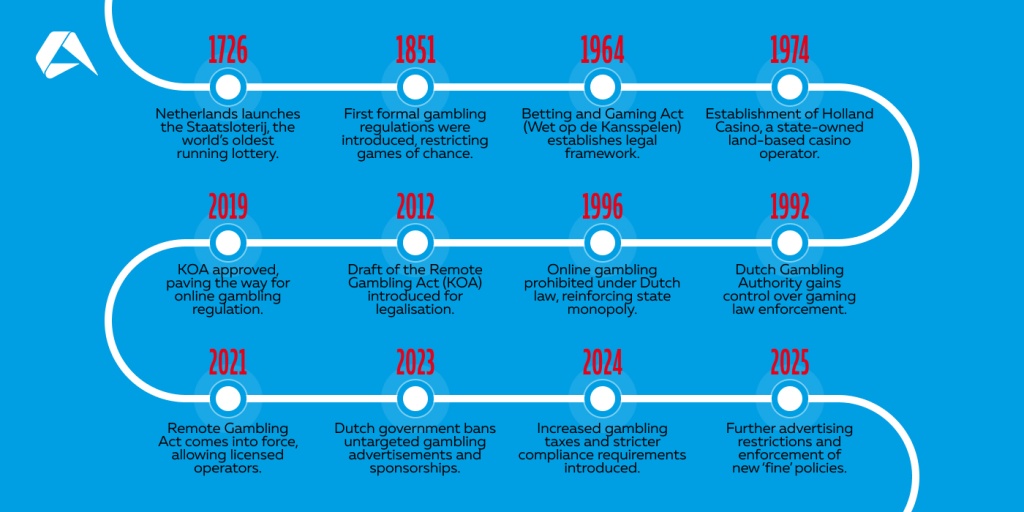
1726: Netherlands launches the Staatsloterij, the world’s oldest running lottery.
1851: First formal gambling regulations were introduced, restricting games of chance.
1964: Betting and Gaming Act (Wet op de Kansspelen) establishes legal framework.
1974: Establishment of Holland Casino, a state-owned land-based casino operator.
1992: Dutch Gambling Authority gains control over gaming law enforcement.
1996: Online gambling prohibited under Dutch law, reinforcing state monopoly.
2012: Draft of the Remote Gambling Act (KOA) introduced for legalization.
2019: KOA approved, paving the way for online gambling regulation.
2021: Remote Gambling Act comes into force, allowing licensed operators.
2023: Dutch government bans untargeted gambling advertisements and sponsorships.
2024: Increased gambling taxes and stricter compliance requirements introduced.
2025: Further advertising restrictions and enforcement of new ‘fine’ policies.
Current Landscape for Gambling in the Netherlands
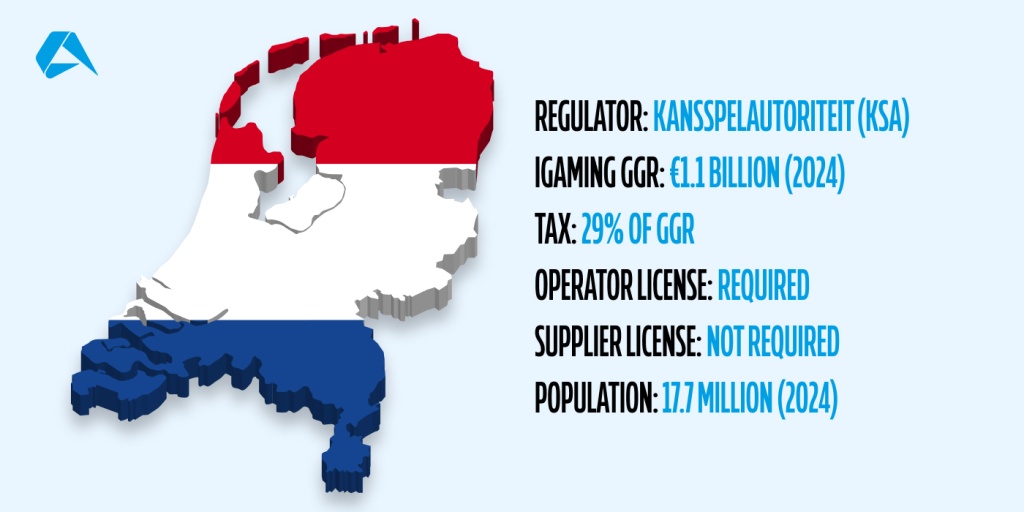
The Dutch gambling market has dramatically transformed over the past few years. Once tightly controlled under a state monopoly, the industry is now open to licensed private operators, bringing the Netherlands in line with other highly regulated European markets. Thanks to the Remote Gambling Act (KOA) of 2021, both local and international companies can legally offer online betting and casino games, provided they meet strict licensing and compliance standards.
To operate legally, iGaming providers must obtain a remote gambling license from the Netherlands Gambling Authority Kansspelautoriteit (KSA). The KSA enforces demanding requirements, including strong AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customer) protocols, responsible gambling tools, and full integration with CRUKS, the country’s national self-exclusion system. Operators must also prove financial stability and adhere to strict advertising and marketing regulations, which have become even more restrictive in 2025.
The cost of noncompliance is high. The KSA has stepped up enforcement, issuing fines of up to €2 million or 10% of an operator’s annual turnover for violations. Unlicensed operators targeting Dutch players face ISP blocks and payment restrictions, making unauthorized market entry a costly gamble.
Adding to these pressures, the Dutch government has raised the gambling tax to 34.2% in 2025, with another hike to 37.8% planned for 2026. These increasing costs mean operators must carefully balance compliance and profitability. Yet, despite the challenges, the Netherlands remains a highly attractive market. Its strong digital infrastructure, tech-literate population, and growing appetite for online gambling make it a lucrative, albeit highly regulated, jurisdiction.
Operational Compliance Requirements for iGaming Platforms
The regulatory framework for online gambling in the Netherlands is one of the most stringent in Europe. Key regulations include:
Licensing
Before offering services to Dutch consumers, all iGaming operators must secure a remote gambling license from the Netherlands Gambling Authority (Kansspelautoriteit - KSA). The comprehensive application process requires operators to demonstrate financial stability and technical compliance with local laws. Operators must also provide a €50,000 financial security deposit to cover potential regulatory infractions.
Player Safety Policies and Tools
Operators must implement responsible gambling measures such as deposit limits, time-based playing restrictions, reality checks, and direct interventions for at-risk players. In addition, all licensed platforms must be integrated with CRUKS (Centraal Register Uitsluiting Kansspelen), the national self-exclusion register, ensuring that individuals who opt out of gambling cannot access regulated sites.
Adherence to AML and KYC Policies
Under Dutch law, operators must conduct enhanced due diligence (EDD) on high-risk players, verify customer identities, and monitor transactions for suspicious activity. Reports of unusual financial behavior must be submitted to the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU-Nederland) to prevent money laundering and financial crimes.
Data Protection and Cybersecurity Compliance
Strict compliance with GDPR and Dutch privacy laws is mandatory. Operators must encrypt player data, implement secure payment processing, and provide full transparency on data handling practices. They must also ensure that all player records are stored in a separate Dutch-based data base (CDB – Control Data Bank) for regulatory monitoring.
Fair Gaming Practices and Technical Audits
To maintain transparency, gambling operators must also undergo regular audits by independent testing agencies to verify that games meet fairness standards. Random Number Generators (RNGs) must be independently certified, and payout percentages (RTP) must be clearly stated and aligned with Dutch legal requirements.
Compliance with Advertising and Marketing Regulations
Since July 1, 2023, the Netherlands has banned untargeted gambling advertisements, sponsorships, and influencer marketing, particularly those aimed at young adults (18–24). New rules require all advertising to be demonstrably targeted at audiences over 24 years old, with affiliates held to the same standards as operators. The Netherlands Advertising Code (RCC) oversees compliance, and violators risk heavy fines.
Licensing Costs, Fees and Taxes
Entering and maintaining compliance in the Dutch gambling market requires a clear understanding of financial obligations, including licensing fees, operational compliance costs, and taxation. Below is a detailed breakdown of the key economic aspects iGaming operators must account for.
Costs of Market Entry for Operators
The KSA oversees licensing for online gambling operators.
-
Application Fee: The initial fee is €48,000, payable upon submission. This fee is nonrefundable, even if the application is rejected.
-
Financial Security Deposit: Operators must provide a financial guarantee of €50,000 to cover potential regulatory fines or penalties.
-
License Duration & Renewal Fees: A standard license is valid for up to five years. While no fixed renewal fee exists, operators must apply for renewal before expiration to ensure continued compliance with updated regulations.
Ongoing Compliance Costs
Beyond licensing, operators must invest in ongoing compliance to remain within Dutch legal requirements.
-
Market Levy: The KSA's regulatory oversight costs are covered by a 1.95% levy on gross gaming revenue (GGR).
-
AML & Responsible Gambling Measures: Operators must allocate funds for KYC procedures, AML compliance, and integration with the national self-exclusion scheme (CRUKS).
-
Annual Audits: Independent testing of gaming systems and RNG certification add to operational expenses.
-
Advertising Compliance: Dutch advertising restrictions demand strict adherence to targeting rules, which may involve legal reviews and compliance consultations.
Tax Obligations
Taxation in the Netherlands is one of the biggest cost factors for gambling operators.
-
Gambling Tax: As of January 1, 2025, the gambling tax has increased from 30.5% to 34.2% of GGR.
-
De Minimis Exemption: Small prizes below €449 are exempt from player taxation.
-
Penalties for Noncompliance: Operators who fail to comply with tax laws or licensing regulations face fines of up to 4% of annual turnover or €600,000 for operators generating under €15 million annually.
DISCLAIMER
Licensing fees, compliance costs, and tax rates are subject to change. For the most up-to-date information, operators should contact the KSA directly or consult the official KSA website.
For specific inquiries, you can reach out to the KSA via email at [email protected] or by phone at +31 (0)70 302 1300
Gambling Regulatory Bodies
The Netherlands maintains a highly structured gambling regulatory framework, carefully monitoring every aspect of the industry, from licensing and taxation to consumer protection. Multiple authorities oversee compliance and enforcement policies that balance market growth with player safeguards and financial integrity.
Kansspelautoriteit

The KSA is the driving force behind gambling regulation in the Netherlands, ensuring operators follow the law and maintain high standards of integrity. It oversees licensing, enforces compliance, and keeps a close watch on responsible gambling measures, advertising rules, and AML policies. Working alongside the Ministry of Justice and Security and the Dutch Tax Authority, the KSA investigates violations, issues fines, and blacklists illegal operators.
For gambling operators, the KSA’s influence is far-reaching. It determines who gets licensed, how they operate, and whether they remain compliant. Strict reporting, responsible gaming, and advertising rules mean operators must continuously align with evolving regulations. Noncompliance can result in heavy fines or license revocation. The KSA also works closely with operators to clarify legal requirements, ensuring they meet stringent AML and consumer protection standards.
Ministry of Justice and Security
The Ministry of Justice and Security is responsible for setting the legal framework governing gambling in the Netherlands. While it does not typically interact with gaming operators, this body collaborates closely with the KSA to draft and implement gambling laws, ensuring all regulations align with broader national policies on consumer protection, anti-money laundering, and market integrity. In addition to overseeing compliance, the Ministry plays a central role in combating illegal gambling operations and ensuring public safety within the sector.
Operators must stay informed about the Ministry's policy changes, as these shifts can lead to new compliance requirements, tax adjustments, or marketing restrictions. However, the KSA remains responsible for day-to-day regulatory oversight.
Dutch Tax Authority (Belastingdienst)

The Belastingdienst is at the heart of the Dutch gambling industry's financial regulation, ensuring operators stay on top of their tax obligations. From gambling taxes on GGR to levies on player winnings, it ensures that the sector contributes its fair share to public funds while supporting responsible gambling initiatives and market regulation.
The Dutch Tax Authority works closely with the KSA and the Ministry of Justice and Security to ensure operators submit accurate tax declarations, meet reporting deadlines, and follow evolving fiscal policies. Deliberate or accidental missteps can lead to audits, fines, or legal action.
Opportunities, Challenges and Outlook
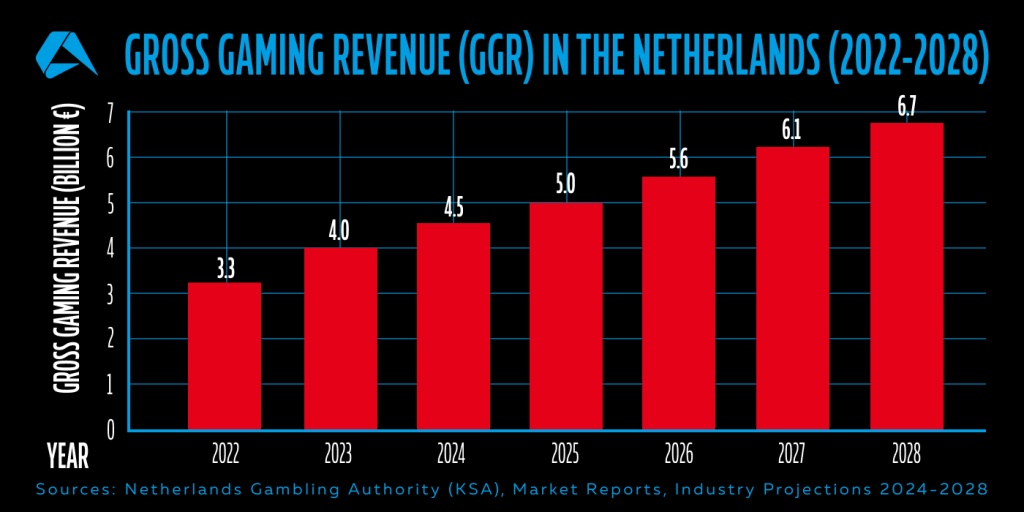
With total GGR reaching €4 billion in 2023, an increase of 21.2% from the previous year, the gambling sector in the Netherlands is experiencing strong momentum, particularly in the online space. Digital gaming alone saw an 8% rise in GGR, reflecting a growing preference for regulated online gambling among Dutch consumers. Notably, in the second half of 2023, 5% of Dutch adults participated in online gambling, and a remarkable 90% of these players placed their bets exclusively with licensed operators, indicating a clear shift toward legal platforms.
Nonetheless, access to one of the world's top eight sports betting markets can be challenging. The KSA has taken a more assertive stance in recent years, particularly on advertising and responsible gaming policies. “Operators must now be more diligent than ever in how they engage with players,” said a spokesperson from the KSA in a recent statement. “The goal is to create a sustainable industry that prioritizes player protection without stifling growth.” This approach has resulted in the introduction of a new ‘fine’ policy, effective from January 2025, which increases penalties for regulatory breaches and heightens scrutiny on advertising practices.
Alongside tightening regulations, the Dutch government has announced an increase in gambling tax rates, rising from 30.5% to 34.2% in 2025, with another hike to 37.8% planned for 2026. While higher taxes are a challenge, they also contribute to a well-regulated market that ensures transparency and fairness. “A strong regulatory environment makes the Netherlands an attractive market in the long run,” gaming policy analyst Dr. Erik Konings added.
Despite these constraints, the Dutch market remains an attractive prospect for operators willing to take the plunge. The population of over 17 million boasts a high internet penetration rate, and consumers are increasingly embracing digital gaming experiences. The rise of mobile betting, AI-driven personalization, and live gaming innovations creates fresh opportunities for new entrants to differentiate themselves in a competitive but still evolving market. Moreover, market saturation has not yet reached the levels seen in other European jurisdictions, meaning there is still room for brands to establish a foothold and build consumer trust.
Looking ahead, further regulatory developments are expected as the Dutch government refines its gambling legislation. A revised gambling bill aimed at strengthening consumer protections and closing loopholes in existing laws is anticipated by late 2025. While this signals an even more controlled operating environment, it also suggests a long-term commitment to market sustainability.
Market Advantages and Disadvantages
Top Advantages
-
Strong Regulatory Framework: Well-defined laws ensure market stability and consumer trust.
-
Legal Access to a Wealthy Market: High disposable income among Dutch consumers.
-
High Player Trust in Regulated Operators: Over 90% of online players use licensed platforms.
-
Rapidly Growing Online Sector: Digital gambling revenues are increasing year-over-year.
-
Early Entry Advantage: The market is still maturing, allowing for strong brand establishment.
Top Market Disadvantages
-
High Gambling Tax Rates: Increased to 34.2% in 2025.
-
Fierce Competition: Market entry requires strong differentiation against established brands.
How to Apply for a Gambling License in Holland
As an iGaming operator looking to enter the Dutch market, obtaining and maintaining a gambling license requires diligent preparation and compliance. Here’s a streamlined step-by-step guide to the process in 2025:
Step 1: Assess Eligibility
A significant application fee is required regardless of whether you are granted a license. For this reason, it is prudent to ensure your business aligns with the strict requirements enforced by the Dutch Gambling Authority. The application fee is nonrefundable, so conducting an internal compliance audit beforehand is strongly recommended to avoid costly delays. Operators should also review Dutch regulations to ensure their business model aligns with the country’s legal framework.
Step 2: Document Preparation
Once eligibility is confirmed, operators must compile all necessary documents to support their application. This includes a detailed business plan, descriptions of gaming products, proof of financial stability, AML procedures, responsible gambling policies, and IT security measures. Furthermore, operators must submit system audits verifying fair gaming practices and ensure technical compliance with Dutch standards. Gaming software and IT infrastructure must undergo independent testing to meet the KSA’s requirements.
Step 3: Submit Application
After compiling all required documents, operators must submit an application through the KSA’s online licensing portal and pay the required fee. The KSA conducts a rigorous evaluation, reviewing financial structures, IT security protocols, AML measures, and responsible gambling tools. The thorough review process includes independent audits to verify software integrity, fraud prevention mechanisms, and adherence to Dutch consumer protection laws.
Step 4: Pass Operational Compliance Audits
Following submission, compliance audits validate game fairness, system security, and adherence to responsible gambling measures. Before proceeding, the KSA may request additional clarifications or impose further compliance checks. Operators should be prepared to demonstrate the effectiveness of their AML strategies and player protection tools at this stage.
Step 5: Register with the Dutch Tax Authority (Belastingdienst)
Operators must register with Belastingdienst before launching operations to ensure full compliance with gambling tax obligations. Moreover, integration with the CRUKS self-exclusion system is mandatory, providing players access to responsible gambling protections. Many applications face delays at this stage due to incomplete CRUKS integration or failure to meet AML reporting standards.
Step 6: Receive License and Maintain Compliance
Once all conditions are met, the KSA grants the gambling license, typically valid for five years. However, obtaining a license is just the beginning. Operators must comply with ongoing regulatory requirements, including financial reporting, periodic audits, and adherence to evolving consumer protection laws. Failure to meet compliance obligations can result in fines, operational restrictions, or license revocation.
Step 7: License Renewal
License renewal is not automatic. Operators must demonstrate continued compliance with updated regulations, including proof of financial stability, responsible gaming measures, and independent audit reports. Planning ahead is essential, as the renewal process requires re-evaluating all compliance frameworks to ensure alignment with Dutch gambling laws.
What’s stopping your brand from capturing a sizable market share in the Netherlands right now?
The Netherlands is a multi-billion-euro market and growing. Get the technology and support you need to navigate it confidently. Schedule a private demonstration with Altenar today and learn what’s possible.
DISCLAIMER
This information is not intended to be legal advice and is solely extracted from public sources. It should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional legal advice, and Altenar does not accept any liability for its use.