Overview The Czech Republic’s Gambling Market: Licensing, Regulation, and Opportunity
The Czech Republic gambling market presents a structured, tightly regulated environment that is increasingly appealing to serious iGaming operators. Moving past earlier decentralised systems, the market is now anchored by the modern Gambling Act (Act No. 186/2016 Coll.), requiring strict adherence to transparency and accountability. Operators must secure a dual-permit licensing regime from the Ministry of Finance (Ministerstvo financí ČR), the key licensing and supervisory authority.
While complexity and high operational standards—such as mandated server localisation within the Czech Republic, substantial security deposits, and tiered Gross Gaming Revenue (GGR) taxes of 30% to 35%—can be barriers to entry, the upside is stability and strong player engagement. In 2023, licensed operations generated over CZK 50 billion (≈ €2 billion) in GGR, highlighting the market’s profitability. Success hinges on robust compliance frameworks, addressing requirements set by bodies like the Czech Customs Administration and the Financial Analytical Office (FAU) for AML enforcement.
Ready to learn how to enter and thrive in Czechia’s iGaming space? Read the full blog below for essential insights.
The Czech Republic might not be the loudest voice in Europe’s gambling conversation, but that’s exactly why it deserves a closer look. Behind the quiet reputation is one of the most clearly defined regulatory frameworks on the European continent.
But clarity doesn’t mean simplicity. This is a market where the details matter. Server locations, capital thresholds, and even your Czech-language support setup can determine whether you get licensed. And yes, taxes are higher than in some markets, but so is the upside: licensing stability, strong enforcement, and a population that engages year-round with sportsbook and casino products.
We’ve done the background research in this article, pulling together the legal, financial, and operational essentials from official sources, and translating them into a language operators understand: risk, reward, and readiness.
DISCLAIMER
This information is not intended to be legal advice and is solely extracted from open sources. It should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional legal advice, and Altenar does not accept any liability for its use.
Gambling in the Czech Republic - A Historical Context
Gambling in the Czech Republic has long walked a line between tradition and regulation, a presence in public life that predates modern oversight by decades. The first official lotteries emerged in 1956 with the founding of Sazka, a state-run operator that still plays a central role in the country’s gambling economy. During the communist era, gambling wasn’t officially endorsed, but it was far from absent. Slot machines operated under the guise of sports club fundraising, and poker circles thrived in private homes, out of sight but rarely out of mind.
Then came the Velvet Revolution of 1989, which brought sweeping economic reforms, and gambling was one of the earliest beneficiaries. As state control faded, slot halls spread rapidly. By the early 2000s, the country had one of Europe's highest concentrations of gaming machines. With licensing powers delegated to municipalities, regulation varied from town to town. Some embraced the revenue. Others tried, often unsuccessfully, to restrict growth.
This decentralized system reached its limit by the mid-2010s. Rising public concern over addiction, tax evasion, and criminal infiltration prompted the state to intervene. In response, the government passed the modern Gambling Act (Act No. 186/2016 Coll.), which introduced a structured licensing model for both land-based and online games. That same year, the tax regime was overhauled (Act No. 187/2016 Coll.), replacing flat fees with tiered GGR-based rates. Over time, these were refined through a series of implementing decrees, including Decree No. 466/2023, which raised compliance expectations and tightened operational reporting.
A Brief Timeline of Events
The Czech gambling sector didn’t take shape overnight. Its current structure is the product of decades of social shifts, political reforms, and regulatory turning points. Here’s an overview of the milestones that got it there:
1956
Sazka is founded, launching national lotteries across Czechoslovakia.
1989
Communism ends. Gambling halls and slot machines flood the market.
1990s
Local councils begin issuing permits with minimal restrictions.
2005
Slot machines outnumber post offices in some Czech towns.
2008
The government starts tightening rules on money laundering and ID checks.
2014
Pressure mounts for national regulation of online gambling.
2016
New gambling law brings licensing rules for land and online operators.
2016
Government scraps fixed fees, taxes profits from gambling instead.
2017
New rules introduced to govern game software and machine safety.
2019
Data handling rules updated for player activity and monitoring.
2023
Operators face stricter reporting and compliance obligations.
2024
Tax rates increase with new financial thresholds.
2025
Fresh proposals seek better AML oversight and player safeguards.
The Current Situation
Today, gambling is not only legal but also tightly regulated. While public attitudes remain mixed, tolerant yet wary, the Czech Republic has gradually positioned itself as a serious, structured market. One shaped not by any single event, but by a long and deliberate transition from local license patchworks to a centralized framework anchored by transparency, tax accountability, and oversight.
At the core of this modern system is a dual-permit licensing regime. Operators looking to enter the market must obtain both an initial permit and a basic license, with separate pathways for each gambling vertical. Online sports betting, virtual games, live dealer casino tables, poker, bingo, and technical games are all permitted under national law, provided the operator is established within the EU or EEA and meets financial, operational, and security requirements.
For sportsbook operators, odds betting and live in-play markets are allowed and widely offered by licensed brands such as Sazka, Fortuna, Tipsport, and Chance. While not listed as a standalone category, esports betting is included under ‘events of public interest’ and has seen growing traction. Further to this, online casinos may host slots, card games, roulette, and dice-based titles, with live casino streams also permitted, provided the studio is hosted in a licensed venue.
The nation's citizens have full access to licensed online sportsbooks and casino platforms, provided they register using a verified payment method and undergo identity verification. Once registered, they can place bets on domestic and international sports and online casino games.
Gambling Authorities and Their Role

Running a legal gambling operation in the Czech Republic means more than just securing a license. Behind every licensed sportsbook or online casino in Czechia is a network of regulators, auditors, and watchdogs. Together, these institutions set the rules and shape how gambling operators run, report, advertise, and handle player data.
Ministerstvo financí ČR (Ministry of Finance)
The Ministry of Finance is the licensing and supervisory authority for all regulated gambling in the Czech Republic, including online betting and casino operations. It grants the initial permit and the basic license, sets reporting and player protection requirements, and maintains the national exclusion register.
Operators interact with the ministry through its secure portal to submit technical documentation, financial reports, player data, and AML declarations. The ministry also handles approvals for certified testing labs and enforces advertising, server location, and game integrity rules. Any operator seeking to enter or stay in the Czech market works directly through this channel.
Celní správa ČR (Czech Customs Administration)
While best known for border duties, the Czech Customs Administration plays an important behind-the-scenes role in gambling oversight. It conducts compliance checks, monitors licensed premises, and supports enforcement of the Gambling Act.
For iGaming operators, this includes verifying technical game integrity, reviewing operational records, and assisting with investigations of AML breaches or unlicensed activity. The administration also collaborates with the Ministry of Finance to identify illegal gambling terminals and monitor remote systems. On a day-to-day basis, its presence may feel indirect, but when audits or investigations arise, this is the agency stepping in with the authority to take decisive regulatory action.
Financial Analytical Office (FAU)
The Financial Analytical Office is the Czech Republic’s financial intelligence unit and the lead body for enforcing AML obligations across gambling operations. Licensed operators must register a contact person with the FAU, report suspicious transactions, and follow strict due diligence thresholds, often from as little as €2,000.
The FAU also issues detailed guidance on politically exposed persons (PEPs), high-risk countries, and electronic verification procedures. Operators are expected to document all risk assessments and retain identity and transaction data for up to 10 years. Under Czech and EU AML law, non-compliance can trigger fines, investigations, or criminal referrals.
Úřad pro ochranu osobních údajů (ÚOOÚ) (Office for Personal Data Protection)
ÚOOÚ enforces data protection compliance under Czech law and the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). For iGaming operators, this means strict obligations around player consent, data retention, breach notification, and cross-border transfers. Operators must ensure that all personal and financial data is processed lawfully, stored securely, and not retained longer than necessary.
Regular audits may be conducted, and failure to comply can lead to penalties or operational suspension. ÚOOÚ also offers public guidance, but expects operators to proactively adopt privacy-by-design principles across platforms, verification systems, and marketing databases, especially where user profiling or behavioral targeting is involved.
Council for Radio and Television Broadcasting (RRTV)
RRTV oversees how gambling is advertised across the Czech Republic's television, radio, and audiovisual media. It sets the ground rules for iGaming operators running brand campaigns or affiliate-driven promotions: no targeting minors, no false impressions of easy wealth, and clear warnings on gambling risks. Ads must not feature underage actors, glamorize betting, or run during youth programming. While RRTV doesn’t license operators, it can impose fines or suspend campaigns that violate content regulations. As advertising scrutiny tightens, especially online, aligning with RRTV’s standards is essential to maintaining public trust and staying on the right side of compliance.
Requirements and Regulations for Market Entry
Entering the Czech iGaming market offers significant opportunities, but operators must adhere to a detailed regulatory framework. The primary challenge lies in meeting stringent technical and operational requirements, which demand considerable preparation and investment.
Key Requirements for iGaming Operators in the Czech Republic include:
1 Legal Entity within EU/EEA
Operators must be established as a legal entity in the Czech Republic or another EU/EEA country. This ensures adherence to European standards and facilitates regulatory oversight.
2 Comprehensive Licensing Process
Obtaining a license involves submitting detailed documentation, including a game plan, technical specifications, and evidence of financial stability. The Ministry of Finance oversees this process.
3 Security Deposit Requirement
Operators are required to provide a financial surety, the amount of which varies based on the type of gambling activity. This deposit covers potential liabilities, including unpaid winnings and taxes.
4 Data Center Localization
All servers handling gambling operations must be located within the Czech Republic. This ensures data integrity and facilitates regulatory access.
5 Czech Language Websites
The gambling platform must be accessible in Czech and provide clear information about the operator, game rules, and responsible gambling measures.
6 Player Registration and Verification
Operators must implement systems to verify the identity and age of players, ensuring compliance with legal age restrictions.
7 Responsible Gambling Measures
To promote responsible gambling, players must have access to features such as self-exclusion options, deposit limits, and timeouts.
8 Technical Equipment Certification
All gaming software and equipment must undergo certification by authorized testing laboratories to secure fairness and compliance with technical standards.
9 Data Reporting Obligations
Operators must provide regular reports on gambling activities, including financial transactions and game outcomes, to the regulatory authorities.
10 Compliance with Advertising Regulations
Marketing and advertising activities must adhere to strict guidelines to prevent targeting minors and to promote responsible gambling.
Note:
These are the current requirements as of January 1, 2024. Operators should consult the full text of Act No. 186/2016 Coll. and related decrees for comprehensive guidance.
License Costs and Tax Considerations
Operating legally in the Czech market requires more than a license. Operators must plan for upfront fees, ongoing taxes, and continuous compliance costs across multiple layers of national legislation.
General Licensing
Central to the Czech Republic’s modern gambling regulatory system is a dual-permit licensing regime. This means that operators must secure two separate approvals:
1. A basic license from the Ministry of Finance covering the gambling activity itself.
2. If operating land-based venues, a gambling premises location license from the relevant municipal authority is required.
This structure is designed to provide both central oversight and local control.
While the Gambling Act does not list specific licensing fees, supplementary legal sources offer a general cost outline. Here's what operators can expect when applying:
| Licence Type | Purpose | Estimated Fee (CZK) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Licence | Certifies that the applicant meets the general conditions | Not specified | Required before any specific activity licence |
| Basic Licence (per game type) | Authorises each type of gambling activity | 5,000 | Valid for up to six years |
| Gambling Premises Location Licence | Required for land-based operations | Varies by municipality | Must first hold the corresponding basic licence |
| Security Deposit (Surety) | Financial guarantee based on tax group | Between 20 million-300 million | The amount depends on the operator's tax group |
| Capital Requirements | Demonstrates financial stability | 5 million | Own capital and asset value minimum |
| Annual Supervision Fees | Covers ongoing regulatory oversight | Varies | Calculated based on scale/type of operation |
Disclaimer:
To obtain precise and up-to-date information on the licensing fees, it is advisable to consult the Ministry of Finance or the municipal authority where the gambling operation will be located. These are the authoritative sources for the latest fee structures and administrative costs.
The Taxation Framework
In the Czech Republic, operators are subject to multiple tax obligations, each governed by specific legislation.
Online Gambling Tax
This tax is levied on Gross Gaming Revenue (GGR), which is calculated as the total amount wagered minus the winnings paid out to players.
The applicable rates are:
-
35% for lotteries and technical games
-
30% for live games, odds betting, totalisator games, raffles, bingo, and small-scale tournaments.
Land-based Tax
Additionally, land-based operators of technical games are subject to a minimum tax of CZK 9,200 per gaming machine per calendar quarter, regardless of actual GGR.
Tax returns must be filed, and payments made quarterly, no later than the 25th day following the end of each calendar quarter.
Corporate Income Tax
Companies operating in the Czech Republic are subject to a corporate income tax rate of 21% on their net profits.
Value Added Tax (VAT)
While gambling services are generally exempt from VAT, operators providing additional services (e.g. food, beverages) may be liable for VAT at the standard rate of 21%.
Ongoing Compliance Costs
Once licensed, iGaming operators in the Czech Republic face a range of recurring compliance expenses tied to regulatory upkeep. These include quarterly financial and GGR tax reporting, external audits of technical systems, and maintaining real-time data connections with the Ministry of Finance. Platforms must also meet strict cybersecurity and player protection standards, often aligned with EU law, requiring regular updates and monitoring.
Annual fees may apply for regulatory supervision, and any material changes to operations, such as new game types or ownership updates, require additional filings and approvals. Staff training, AML protocols, and software certification must also be maintained to avoid penalties or suspension.
Costs vary by scale, but ongoing compliance is a constant and non-negotiable operational reality.
Market Opportunities and Limitations
The Czech Republic isn’t typically one of the first names dropped in European gambling circles, but perhaps it should be. With a population of over 10.5 million and a longstanding affinity for sports and gaming, the country has quietly developed into a market worth watching. In 2023, licensed operators generated more than CZK 50 billion (≈ €2 billion) in gross gaming revenue, with online channels making up nearly half of that figure, according to data cited by Vixio GamblingCompliance.
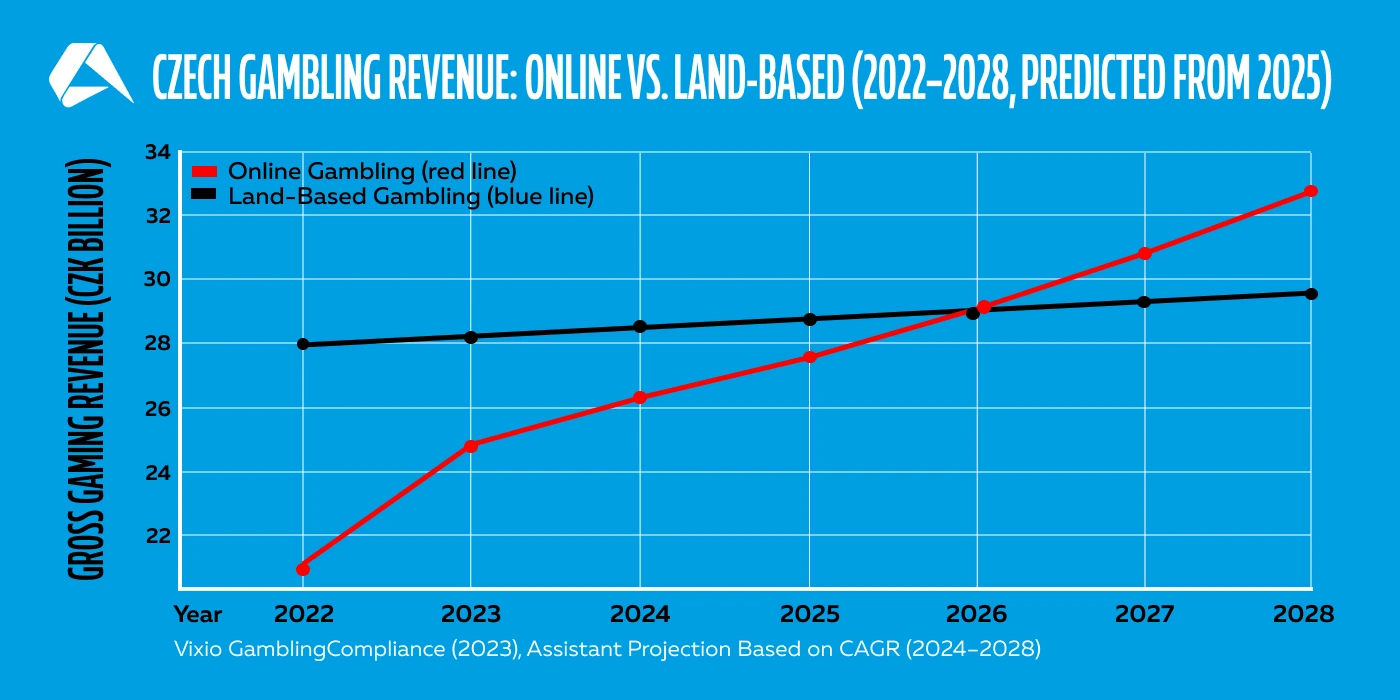
Online casinos and sports betting have both been legal since 2017, but the real shift came with a wave of regulatory updates in 2023 and 2024 that signaled the government’s intention to refine rather than restrict the market. A more responsive licensing system, updated technical requirements, and clearer rules around data reporting are helping to establish a transparent, structured environment that appeals to serious operators.
Barriers to entry exist, including a demanding certification process and financial guarantees, but these are increasingly viewed as filters rather than hurdles among serious operators in Europe. With the rise of more sophisticated digital infrastructure, including remote registration and expanded payment systems, the market is evolving at a healthy pace. With recent reforms now in force, tightening advertising rules and raising tax rates, operators with strong compliance frameworks and a deep understanding of local conditions are well placed to endure and outperform. It’s not a frontier market, for sure, but it can be a profitable one for the right brands.
Market Pros and Cons
What makes the Czech Republic worth a closer look? These defining advantages and strategic considerations shape the current operating climate for sportsbook and casino brands evaluating market entry or expansion possibilities.
Market Advantages
Expanding Online Segment
Online GGR continues to grow, with a strong interest in sportsbooks and casinos.
Strong Player Demand
A tech-literate, iGaming-friendly population fueling steady online growth.
Structured Legal Framework
Clear licensing laws and centralized oversight minimizing regulatory guesswork.
Digitally Connected Players
High internet penetration and mobile usage supporting digital-first operations.
Open to EU/EEA Operators
No local ownership requirement. EU-based companies can apply directly.
Flexible Licensing Structure
No cap on license numbers, with multi-year durations and renewals.
Market Disadvantages
Steep Entry Costs
High security deposits and equity thresholds can deter smaller firms.
Advertising Restrictions Tightening
Recent reforms may limit promotions and player acquisition strategies.
How to Apply for a Gambling License in the Czech Republic
The following steps outline the key legal, financial, and technical requirements under law for international iGaming operators wishing to obtain a gaming license in the Czech Republic.
1. Verify Eligibility as a Legal Entity
Ensure your company is a legal entity registered in the Czech Republic, another EU member state, or an EEA country, with a transparent ownership structure and a clean criminal record.
2. Prepare Required Documentation
Gather necessary documents, including proof of legal status, organizational structure, financial statements, and evidence of sufficient capital and assets.
3. Submit Application for Initial License
Apply to the Ministry of Finance for an initial license, certifying that the general conditions for operating gambling activities are met.
4. Apply for a Basic License for Each Game Type
For each gambling activity (e.g. odds betting, technical games), submit a separate application for a basic license to the Ministry of Finance.
5. Provide Financial Surety
Deposit a financial surety with the Ministry of Finance, either as a bank guarantee or funds in a special account, the amount of which depends on the operator's tax group.
6. Implement Technical and Operational Requirements
Ensure compliance with technical standards, including real-time data sharing with the Ministry, and establish the necessary AML and player protection measures.
7. Undergo System Testing and Certification
Have your gambling systems and software tested and certified by an accredited testing body to ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
8. Establish Player Registration and Verification Processes
Implement procedures for player registration, including identity and age verification, and ensure mechanisms for self-restricting measures are in place.
9. Launch Operations Upon License Approval
Once all licenses are granted and compliance measures are verified, commence operations in accordance with the approved game plans and regulatory requirements.
For Official Licensing Guidance
Operators seeking to apply for a gambling license in the Czech Republic should contact the national regulator directly for authoritative guidance on licensing procedures, documentation requirements, and ongoing compliance obligations.
All applications and inquiries should be directed to:
Ministry of Finance of the Czech Republic
Department 73 – Procedural Agendas and Gambling Regulation
Letenská 15, 118 10 Praha 1
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +420 257 041 111
Official Website: www.mfcr.cz
For full legal references, consult Act No. 186/2016 Coll. on Gambling and Act No. 187/2016 Coll. on Gambling Tax, both available via the Ministry’s official site.
Ready to enter the Czech market with confidence? Before you file your license application, explore an iGaming platform that already meets Czech regulatory standards.
Book a personalized demonstration today and discover how Altenar supports you every step of the way.
DISCLAIMER
This information is not intended to be legal advice and is solely extracted from open sources. It should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional legal advice, and Altenar does not accept any liability for its use.













