Overview Gambling Laws in Mexico: Regulation and Legality
Mexico's gambling industry operates within a complex and evolving legal framework. While gambling is permitted after obtaining corresponding permission from competent Mexican authorities, the sector is not yet fully developed due to existing laws and historical influence from the Catholic Church. Despite these limitations, the number of gambling establishments has significantly increased, from approximately 200 to around 800.
The General Directorate of Games and Drawings, under the Ministry of the Interior, manages, authorises, and controls wagering games and lotteries, operating under the Federal Gaming and Sweepstakes Act of 1947. Commonly allowed games include blackjack, roulette, baccarat, sports betting, and various lotteries.
The legality of internet gambling is notably ambiguous, as the original Gambling Law was too general and lacks a specific legal definition for online gambling. Although Mexican citizens can legally gamble at online casinos in other countries, direct operations by foreign cross-licensed casinos within Mexico are considered illegal. Despite this regulatory uncertainty, online gambling continues to grow in popularity. Further legislative clarification is needed to attract investment and fully legalise the substantial revenue generated from the online sector. Importantly, minors under 18 are strictly prohibited from gambling, and online casinos are encouraged to promote responsible gambling practices. This evolving landscape suggests a sector with significant potential for further legislative development.
If you're exploring the potential of launching or expanding your iGaming operation in Mexico, you're not alone. With one of the largest gambling markets in Latin America and a population passionate about sports, the country offers strong commercial appeal for iGaming operators. But while the opportunity is clear, the route to market isn’t always straightforward.
From navigating licensing requirements to understanding taxation and market trends, this article explores the key factors shaping Mexico’s betting market and what operators must get right to succeed.
DISCLAIMER
This information is not intended as legal advice and is solely drawn from open sources. It should not be relied on as a substitute for professional legal advice, and Altenar does not accept any liability for its use.
The History of Gambling in Mexico
Gambling in Mexico has a long and eventful past, stretching back to pre-Hispanic civilizations. The Aztecs were known to wager on patolli, a dice-based game played on a cross-shaped board, where wealth could be won and lost in the blink of an eye. Despite Spanish colonization introducing stricter moral codes, games of chance never truly disappeared; they simply went underground or took new forms.
Fast-forward to the 19th century and gambling houses flourished under President Porfirio Díaz, bringing European-style casinos to the country’s social elite. Still, after the Mexican Revolution, attitudes hardened. The government took a firm stance against gambling, leading to the introduction of the Federal Law of Games and Raffles (Ley Federal de Juegos y Sorteos) in 1947. This sweeping law outlawed most forms of gambling, shutting down casinos and betting halls across the country.
For decades, Mexico’s gambling industry remained in legal limbo. While lotería (a traditional bingo-style game) was deeply ingrained in Mexican culture, more formal betting operations had to find loopholes to survive. That changed in 2004 when the government introduced regulations clarifying the 1947 law, allowing for licensed casinos, sportsbooks, and online gambling operations under controlled conditions.
By the 2010s, online gambling had gained significant traction, prompting further discussions on regulation. However, in 2023, a presidential decree imposed tighter restrictions on slot machines, online casinos, and third-party betting skins, reshaping the industry once again.
Today, gambling in Mexico is delicately balanced. It is deeply embedded in the country’s culture while operating within a constantly evolving regulatory framework. Understanding the market's past is essential for operators looking to enter or expand.
Timeline of Events
Here's a timeline of some of the most significant moments in Mexico’s gambling history:
1770: Launch of the Royal New Spain, Mexico's first official lottery.
1863: Establishment of Casino Español de México in Mexico City.
1928: Opening of Agua Caliente Casino and Hotel in Tijuana.
1935: President Cárdenas enforces a nationwide ban on gambling.
1947: Enactment of the Federal Law of Games and Raffles.
1978: Pronósticos para la Asistencia Pública lottery established.
2004: Provisions allow casino and sportsbook operations.
2018: Bet365 and other international brands enter the market.
2021: Betsson partners with Big Bola Casinos.
2023: Presidential decree restricts slot machines and online casinos.
The Current Situation for iGaming in Mexico
Gambling in Mexico is a game of shifting rules for both operators and bettors. Although the market has long been one of Latin America’s largest, recent changes have redrawn its boundaries, making it more important than ever to understand what is permitted and what is prohibited.
While the Federal Law of Games and Raffles has been in place since 1947, its interpretation has shifted over the years, with major regulatory updates in 2004 and, more recently, 2023, with the latter bringing significant restrictions that are reshaping the sector.
Sports betting remains one of the safest and most viable routes for those focused on online gambling. It operates under local licensing requirements and continues to thrive, particularly around major soccer tournaments, where betting activity intensifies. Online casinos, however, face an uncertain future. The 2023 decree imposed a sweeping ban on online slot machines, roulette, dice, and card-based casino games, though existing license holders may continue offering these products until their permits expire, and new or renewed licenses will face tighter restrictions.
For international operators, market access has always required a partnership with a locally licensed company, but even this route is narrowing. Recent regulatory changes have banned third-party “skin” agreements, meaning foreign brands must rethink their approach if they want a slice of the Mexican market.
Despite these legal hurdles, Mexico remains Latin America’s second-largest gambling market after Brazil. There’s no doubt about the appetite for betting in this country, but unlicensed operators continue to muddy the waters, prompting ongoing enforcement efforts. A strategic, well-informed approach is more important than ever for those looking to enter the market. Success will depend on meeting Mexican regulations, reducing risks and simplifying market entry with localized solutions. Securing the right partnerships and understanding where the real opportunities lie is key in this high-potential but increasingly complex market.
Mexican Regulatory Bodies and Their Role
Several regulatory bodies oversee the gambling sector in Mexico. Each is responsible for different aspects of compliance and enforcement. Understanding their functions helps navigate legal requirements and maintain smooth business operations.
Secretaría de Gobernación (SEGOB)
The Secretaría de Gobernación is Mexico's Ministry of the Interior. It oversees various aspects of internal governance, including the regulation of gambling activities. Through its subordinate body, the Dirección General de Juegos y Sorteos (DGJS), SEGOB authorizes, monitors, and controls games of chance and raffles nationwide. This includes issuing permits for casinos, betting establishments, and lotteries and ensuring that all operations comply with the Federal Gaming and Raffles Law.
SEGOB collaborates closely with other agencies, such as the Unidad de Inteligencia Financiera (UIF), to prevent money laundering within the gambling sector. By maintaining firm oversight, SEGOB aims to promote fair play and protect consumers, thereby encouraging a transparent and accountable gambling environment in Mexico.
Dirección General de Juegos y Sorteos (DGJS)
The Dirección General de Juegos y Sorteos sits at the center of Mexico’s gambling industry, keeping a watchful eye on everything from casino floors to online betting platforms. As a division of SEGOB, it holds the authority to approve licenses, monitor compliance, and enforce regulations under the Federal Gaming and Raffles Law (Decree No. 728).
For operators, the DGJS is the gatekeeper. No casino, sportsbook, or lottery can legally function without its authorization. But it doesn’t stop there. Regular inspections, compliance checks, and fraud prevention measures ensure that only those playing by the rules remain in the Mexican market. Working alongside agencies like the Unidad de Inteligencia Financiera, it also helps crack down on financial crime, reinforcing transparency and accountability across the sector.
Unidad de Inteligencia Financiera (UIF)
The Unidad de Inteligencia Financiera, operating under Mexico's Secretaría de Hacienda y Crédito Público (SHCP), is the nation's Financial Intelligence Unit tasked with combating financial crimes, including money laundering and terrorist financing. Established in 2004, the UIF receives, analyzes, and shares information related to suspicious financial activities. In the gambling sector, the UIF collaborates closely with regulatory bodies such as DGJS and SEGOB to monitor and prevent illicit financial activities within gaming operations.
By enforcing compliance with anti-money laundering regulations, the UIF ensures that gambling operators implement strong internal controls and report any suspicious transactions. With growing international pressure on financial transparency, the UIF’s role is more significant than ever, making it a key player in shaping the future of Mexico’s regulated gambling industry.
Regulatory Requirements for iGaming Operators
Mexico’s regulatory framework establishes clear guidelines for private sportsbook operators. Ensuring compliance with established laws enforced by SEGOB and DGJS is necessary for entities seeking to enter and maintain a legal presence in this market. Here are the key legal requirements:
1. Requirement Under the Federal Gaming and Raffles Law
Mexico’s gambling industry is regulated under the Ley Federal de Juegos y Sorteos (LFJS) and its regulations, which require all operators to obtain authorization from DGJS under a land-based operator’s existing license. No standalone online-only licenses exist.
2. Foreign Access Requirement
With sublicensing agreements no longer permitted under Mexico’s updated regulations, foreign operators must now seek compliant entry via licensed Mexican entities. Future market access depends on direct partnerships and regulatory alignment.
3. Physical Presence in Mexico
Only Mexican legal entities can apply for gambling licenses. This requirement effectively necessitates that operators establish a physical presence within the country to comply with corporate and operational obligations.
4. Server Hosting and Data Storage
As outlined in Article 38 of the 2004 Regulations, gaming equipment, including servers and other essential infrastructure, must be located within Mexico. This territorial requirement helps support regulatory oversight and aligns with national data protection and operational control standards.
5. Compliance with Advertising and Promotion Rules
According to Article 9 of the Reglamento de la Ley Federal de Juegos y Sorteos (2004), gambling advertisements must not encourage excessive participation, mislead the public, or target minors. All ads must clearly state the operator’s license number and include messages promoting responsible gambling. Promotional offers also require prior approval from the DGJS.
6. Anti-Money Laundering Compliance
Operators are classified as obligated parties under Mexico’s AML laws and must report high-value transactions (equal to or greater than x645 the minimum wage) to the UIF. They must also conduct Know Your Customer and risk-based due diligence on players.
7. Taxation Registration
As part of the licensing requirements, gambling operators in Mexico must register with the Servicio de Administración Tributaria (SAT), the country's tax administration service. This registration is essential to comply with federal tax obligations and potentially state-level gaming taxes, which vary by region.
8. Responsible Gambling Measures
Operators must implement self-exclusion programs, deposit limits, and responsible gambling messaging in accordance with Mexican consumer protection laws. They must also periodically report problem gambling data to DGJS.
9. License Renewal and Audits
Mexican gambling permits are valid for one to 15 years and can be renewed for the same period if all obligations are met. While annual renewal isn’t required, operators must maintain full compliance throughout the license term to avoid penalties, suspension, or revocation.
License Costs and Tax Considerations
The cost of entering Mexico’s gambling sector isn’t fixed, yet it is manageable for those who do their homework. From permits to taxes, this section outlines the key financial and administrative obligations for operators seeking long-term success.
Licensing Costs:
-
Application and Licensing Fees: The specific fees for obtaining a gambling license in Mexico can vary depending on the type of gambling activity and the terms set by the Ministry of the Interior (Secretaría de Gobernación). Operators must apply via a Mexican legal entity and are advised to consult directly with the DGJS for precise fee structures.
-
Set-Up and Administrative Costs: Establishing a gambling operation in Mexico involves various expenses, including incorporation, notary fees, legal services, and administrative costs. These expenses can vary widely based on the size and scope of the operation.
Types of Gambling Licenses and Authorizations
Under the Reglamento de la Ley Federal de Juegos y Sorteos (Regulations of the Federal Gaming and Raffles Law), Mexico recognizes four primary types of gambling licenses:
-
Licenses for Land-Based Establishments: These permits authorize the opening and operation of facilities such as horse and greyhound racetracks, jai alai fronton arenas, remote betting centers (sportsbooks), and rooms for drawing numbers or symbols. These licenses encompass activities including live gaming, slot machines, and online gaming. Only Mexican commercial companies, duly constituted under Mexican law, are eligible to obtain these licenses.
-
Licenses for National Fairs: Permits granted for organizing gambling activities during national fairs, such as the Feria Nacional de San Marcos.
-
Licenses for Temporary Events: These cover the opening and operation of horse racetracks in temporary scenarios and cockfighting betting events.
-
Licenses for Raffles: Authorizations required to conduct various types of raffles and lottery games.
It's important to note that online gambling operations are not granted through standalone licenses. Instead, operators must obtain specific authorizations under an existing land-based license. According to Article 12 Bis, Section III of the 2004 Regulations, online gambling services can only be offered by entities that hold a valid land-based license and have received explicit authorization from the Dirección General de Juegos y Sorteos (DGJS) to conduct online operations.
Furthermore, sportsbooks and land-based casinos require specific approval from the local municipality, which must consent to the installation and operation of such establishments.
For detailed information and guidance on the licensing process, operators are advised to consult directly with the DGJS and refer to the official regulations:
Tax Considerations:
-
Income Tax (Impuesto Sobre la Renta - ISR): Legal entities operating in Mexico are subject to a corporate income tax rate of 30% on their taxable income, which is calculated by deducting authorized expenses from total income.
-
Special Production and Services Tax (IEPS Ley del IEPS – Article 2, Section II): A 30% tax is levied on the total amount of bets received by operators. This tax applies to all forms of gambling that require a permit under Mexican law.
-
Local (state-level) Taxes: Some Mexican states impose additional taxes or levies on gambling operators and/or casino users, depending on the state and location. These taxes can vary by region and may include additional levies on gambling revenues or specific fees per gaming machine installed.
DISCLAIMER
This information is for general guidance only and does not constitute legal advice. Operators should consult qualified legal counsel and refer to official legislation before making regulatory or commercial decisions.
10 Key Steps to Securing a Gambling License in Mexico
Entering Mexico’s regulated gambling sector legally requires an understanding of the official process. This 10-step guide outlines what operators must do to apply, qualify, and maintain compliance:
Step 1. Establish a Mexican Legal Entity
Form a Mexican corporation, as only entities incorporated under Mexican law can apply for gambling permits.
Step 2. Prepare Comprehensive Documentation
Compile required documents, including corporate bylaws, tax registrations, and detailed business plans outlining the proposed gambling operations.
Step 3. Submit Application to DGJS
File your application with the Dirección General de Juegos y Sorteos (DGJS), providing all necessary documentation and adhering to specified guidelines.
Step 4. Undergo Financial and Security Evaluations
Participate in assessments conducted by relevant authorities to verify financial stability and compliance with security protocols.
Step 5. Obtain UIF Clearance
Secure approval from the Unidad de Inteligencia Financiera (UIF) to ensure adherence to anti-money laundering regulations.
Step 6. Register with SAT
Enroll with the Servicio de Administración Tributaria (SAT) for tax obligations, including income and special production taxes.
Step 7. Implement Data Protection Measures
Align operations with the Instituto Nacional de Transparencia, Acceso a la Información y Protección de Datos Personales (INAI) standards for data privacy.
Step 8. Comply with CNBV Requirements
Meet the Comisión Nacional Bancaria y de Valores (CNBV) standards for financial transactions and reporting.
Step 9. Await DGJS Approval
After a thorough review, receive your gambling license from the DGJS, authorizing legal operation within Mexico.
Step 10. Maintain Ongoing Compliance
Regularly submit required reports and adhere to all regulatory obligations to ensure license retention.
DISCLAIMER
This process is not explicitly codified step-by-step in law. The process above is an overview for informational purposes only and may not reflect all current legal or procedural requirements. Operators should consult directly with DGJS or qualified legal counsel to confirm exact licensing procedures and conditions in Mexico.
Opportunities and Future Outlook
Mexico's online gambling market is rapidly expanding. Projections indicate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.64% from 2023 to 2033, potentially reaching approximately USD 3.89 billion by 2033. This growth is largely driven by the nation's deep-rooted passion for sports, particularly soccer. Domestic leagues like Liga MX captivate millions, while international tournaments such as the NBA and top European soccer leagues command significant attention.
With this strong sporting culture, it’s no surprise that betting has become a mainstream activity among Mexican consumers. TGM Research highlights this trend, reporting that according to the results of the TGM Sports Betting Survey conducted in Mexico in October 2022, 40% of the population was involved in sports betting activities within the last 12 months. It is also interesting to note that sports betting in Mexico is often a shared activity, with friends and family placing wagers together. This communal aspect enhances the experience, making betting a form of social entertainment rather than just a financial pursuit.
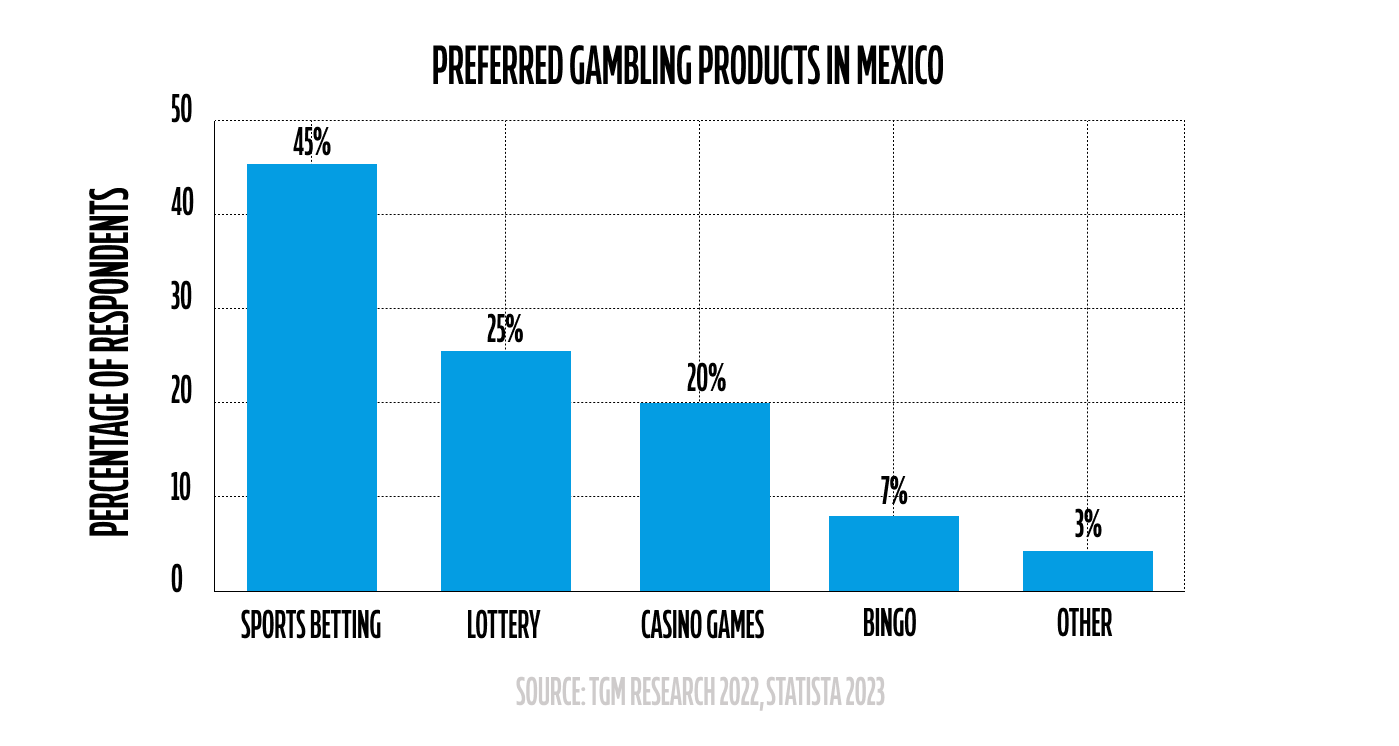
However, despite the market advantages, the licensing process and the tax environment present some significant hurdles for those seeking to break into Mexico. Operators are subject to a 30% tax rate on GGR, which requires careful financial planning. Despite this, the market's potential profitability remains enticing, especially given the projected growth and increasing user engagement.
Mobile gaming has also emerged as a significant driver of this growth. With a high rate of smartphone ownership and mobile internet usage, operators have the chance to tap into a web-savvy gaming community that values convenience and accessibility. This shift toward mobile platforms aligns with global trends and emphasizes the importance of optimizing user experiences for handheld devices.
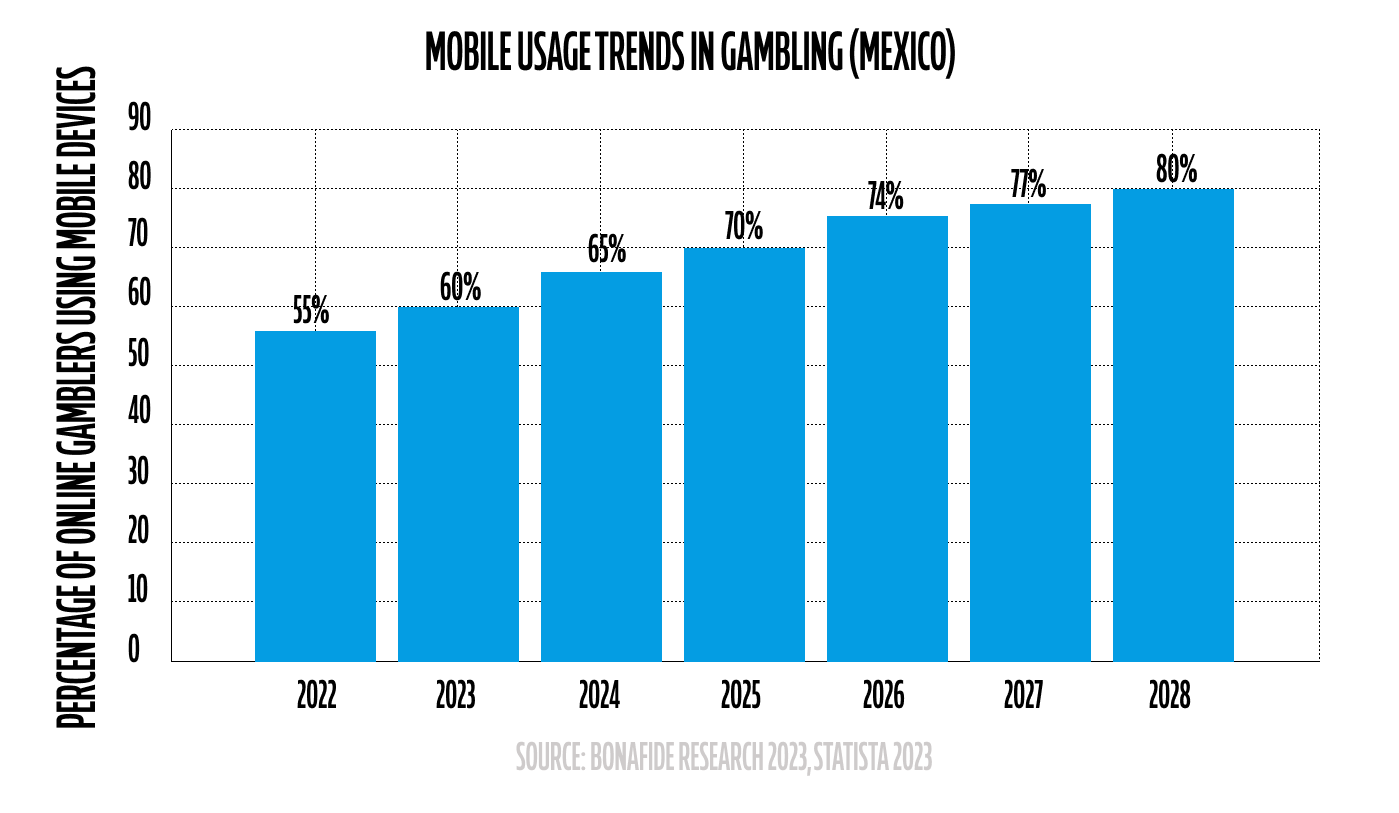
Looking ahead, the Mexican market is positioned for further evolution. As technology advances, innovations such as live betting and personalized gaming experiences are expected to gain more traction. Operators who can adapt to these trends and cater to regional preferences stand to benefit immensely. However, staying abreast of regulatory changes and maintaining compliance will be integral to sustained success in this market.
Pros and Cons of the Mexican market
Before entering Mexico’s gambling market, operators must assess the rewards alongside the challenges to build a sustainable business strategy.
Market Advantages
Expanding Player Base: A fast-growing online gambling market with increasing user engagement and revenue potential.
Strong Sports Betting Culture: Soccer, basketball, and horse racing fuel high betting activity, with Liga MX and international leagues driving interest.
Mobile-Driven Growth: High smartphone penetration provides opportunities for mobile-first betting and gaming platforms.
Local & Global Operator Presence: Established market players coexist with new entrants, proving the industry’s viability.
Regulated Industry Framework: A structured regulatory environment provides legal clarity for licensed operators.
Market Disadvantages
High Taxation: A 30% tax on GGR creates financial pressure on operators.
Regulatory Shifts: Recent decrees have imposed restrictions on certain gaming products, requiring adaptability.
Complex Licensing Process: Strict application requirements and compliance demands can be challenging for newcomers.
Winning Game Plan for iGaming Success in Mexico
Breaking into Mexico’s gambling market can feel like trying to score a goal blindfolded. The rules are there, but interpreting them, especially as a foreign operator, isn’t always straightforward. Adjusting to rapidly evolving regulatory changes and staying compliant with advertising, tax, and data requirements, operators face more than a few hurdles just to get started, let alone scale.
That’s where Altenar steps in.
We don’t just provide sportsbook software. We help build sustainable businesses. From the moment a partner begins onboarding, our full-service platform is engineered to support long-term growth in Mexico’s unique environment. Everything is built for flexibility. Whether an operator needs a custom front end or a high-performance back end that supports local preferences, our modular setup adapts easily, no matter how the market shifts.
But technology isn’t the only piece of the puzzle. Regulations in Mexico can change quickly, and operators need a partner who can help them stay on top. Altenar’s solutions are designed to comply with national standards, and compliance is built into our technology, making it easier for iGaming professionals to comply with local rules and avoid costly setbacks.
For players, we keep things exciting, offering pre-match and in-play betting, esports, player props, and bet builders tailored specifically for Mexico’s sports-loving audience. Whether it’s betting on Liga MX, the NBA, or top-tier European soccer, we’ve got the most popular markets covered with official data feeds that boost margins and strengthen user trust.
And when operators need support, it’s never far away. With round-the-clock trading and risk services, Altenar doesn’t just keep sportsbooks running — we help them win!
Mexico’s regulations don’t need to slow you down. Book a personalized demonstration today and see how Altenar’s locally optimized solutions simplify compliance while keeping your sportsbook competitive, scalable, and market-ready.
DISCLAIMER
This information is not intended as legal advice and is solely drawn from open sources. It should not be relied on as a substitute for professional legal advice, and Altenar does not accept any liability for its use.













